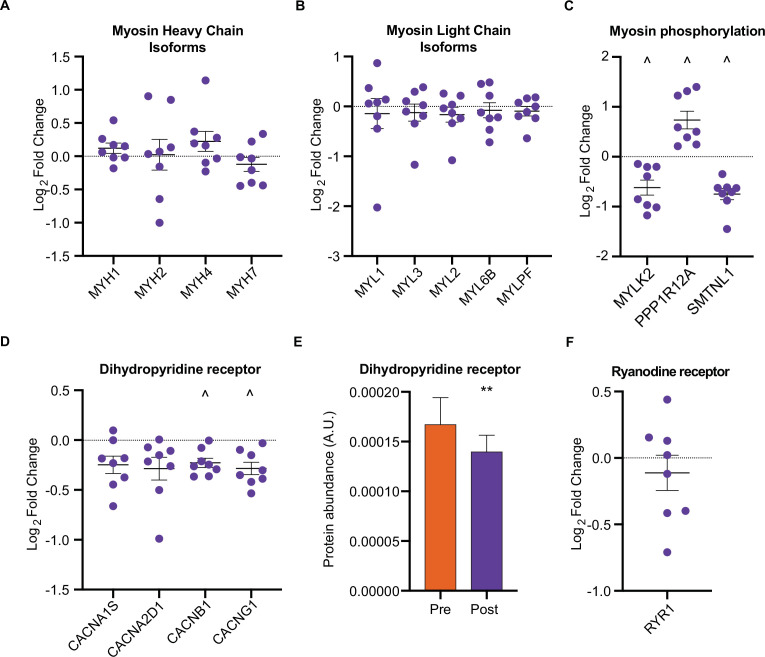
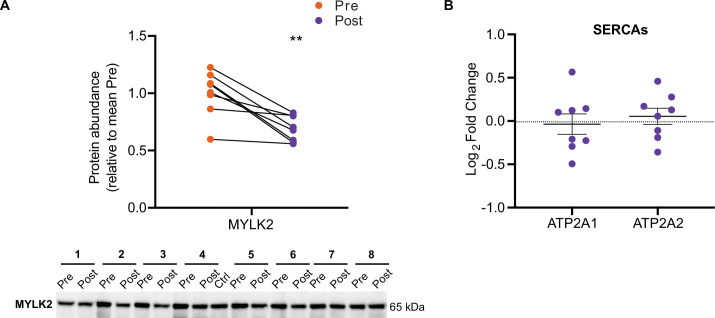
Figure 3. HIIT regulates proteins involved in skeletal muscle calcium sensitivity and handling HIIT did not alter the abundance of myosin heavy chain (MYH1: MyHC2x, MYH2: MyHC2a, MYH4: MyHC2x, MYH7: MyHCβ; A) or light chain (B) isoforms.
(C). HIIT regulates proteins controlling myosin phosphorylation. (D). HIIT reduces abundance of subunits of the dihydropyridine receptor. (E). Summed total protein abundances display downregulation of the dihydropyridine receptor. (F). HIIT does not alter the abundance of ryanodine receptor 1. Summary statistics are mean ± SEM (n=8). ^ FDR <0.05. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001.