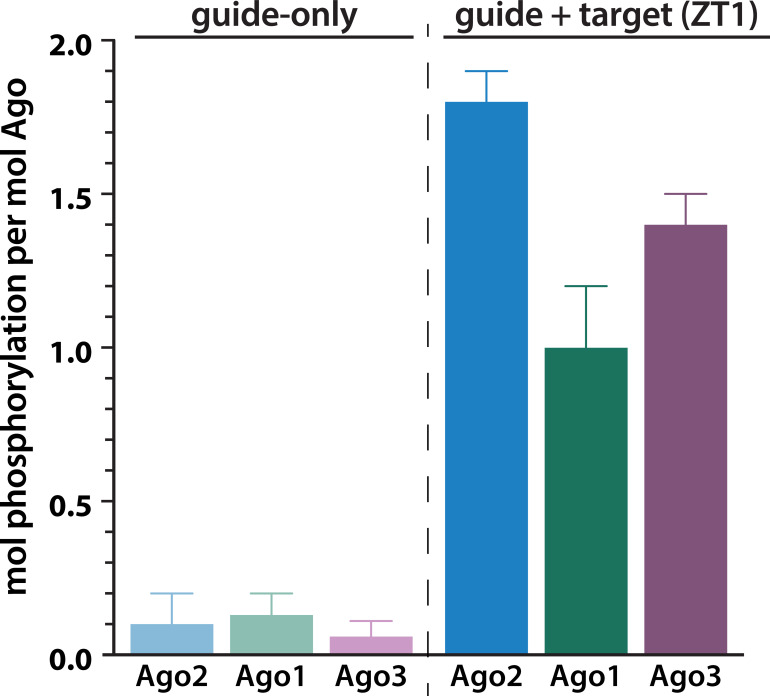
Figure 1. Target binding triggers phosphorylation of the hAgo2 eukaryotic insertion (EI).
(a) Conservation of the EI in eukaryotic miRNA-handling Argonaute proteins. Phosphorylatable residues are highlighted in orange. The four serines are highly conserved in higher eukaryotes, while the threonine is specific to hAgo2. Residue numbering is based on hAgo2. Hs, Homo sapiens; Ce, Caenorhabditis elegans; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster; Mm, Mus musculus; Pf, Pyrococcus furiosus; Tt, Thermus thermophilus. (b) Guide/target pair schematic for miR-200 and a 30-mer target RNA (ZT1) corresponding to a natural and validated miR-200-binding site located in the 3’ UTR of ZEBT1. Nucleotides in the target complementary to the miR-200 seed sequence are labeled in red and the seed and 3' supplementary pairing regions are indicated. (c) Target binding, but not guide binding, dramatically increases CK1a-mediated phosphorylation of hAgo2 as measured by in vitro phosphorylation assays using the guide/target pair shown in b. Quantification of phosphorylation was done by liquid scintillation and comparison to a spotted ATP standard. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error (SE) for three technical replicates.