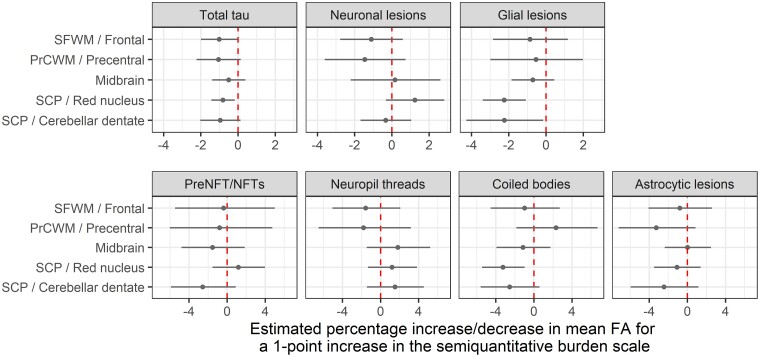
Figure 4.
Relationship between tau lesion scores and DTI-FA. The forest plots display point estimates and 95% confidence intervals for the effect of a one-unit increase in semiquantitative score on fractional anisotropy (FA). Estimates are expressed in terms of percentage differences and come from the PMLE approach. Confidence intervals not crossing the line of null effect (dashed vertical line) are considered significant at P < 0.05. A one-unit increase in total tau burden of the red nucleus was associated with ∼1% lower FA in the superior cerebellar peduncle (P = 0.02). Furthermore, a one-unit greater glial lesion count in the red nucleus (P < 0.001) and cerebellar dentate (P = 0.04) were associated with ∼2% reduction in FA in the superior cerebellar peduncle, with the association in the red nucleus apparently driven by coiled bodies (P = 0.008). DTI = diffusion tensor imaging; FA = fractional anisotropy; NFT = neurofibrillary tangle; PrCWM = Precentral white matter; preNFT = pretangles; SCP = superior cerebellar peduncle; SFWM = superior frontal white matter.