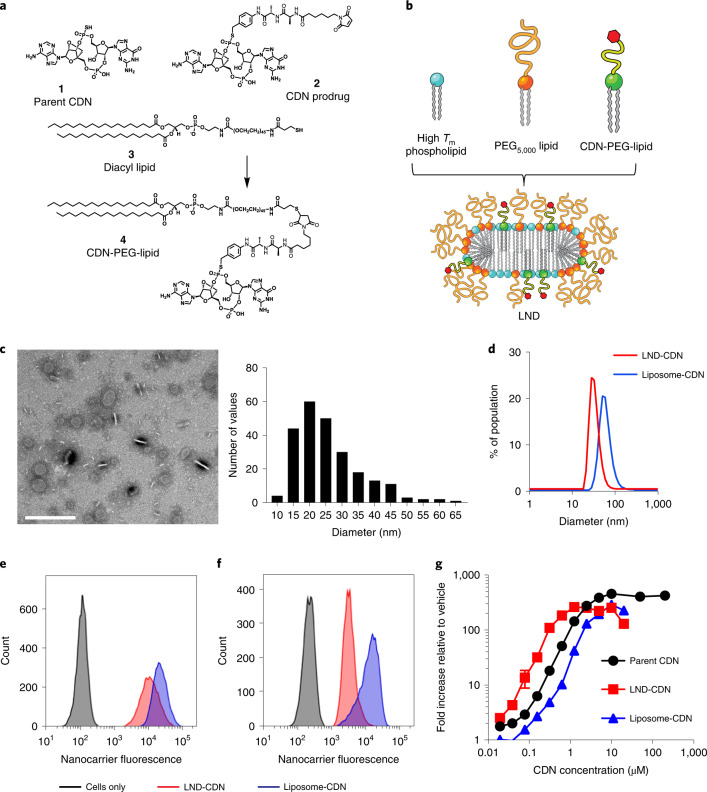
Fig. 1. Design and characterization of nanoparticles for STING agonist delivery.
a, Chemical structures of the parent CDN STING agonist (1), CDN prodrug (2), diacyl lipid (3) and CDN-PEG-lipid (4). b, Schematic of LND containing CDN-PEG-lipid. c, Negative stain transmission electron micrograph of LND-CDNs and histogram of measured LND diameters. Scale bar, 200 nm. This experiment was performed once. d, Dynamic light scattering analysis of LND-CDN (red) and liposome-CDN (blue) particle size distributions. e,f, Representative flow cytometry histograms showing uptake of fluorescent LND-CDN (red) or liposome-CDN (blue) by RAW-ISG cells (STING reporter cell line) (e) or MC38 tumour cells (f) following 24 h incubation at 37 °C with 5 µM CDN in each formulation. g, Dose–response curves showing STING activation in RAW-ISG reporter cells as measured by bioluminescence reporter relative to the vehicle-treated control following 24 h stimulation at 37 °C. Data are presented as mean values ± s.e.m. with n = 4 biologically independent samples for each concentration tested.