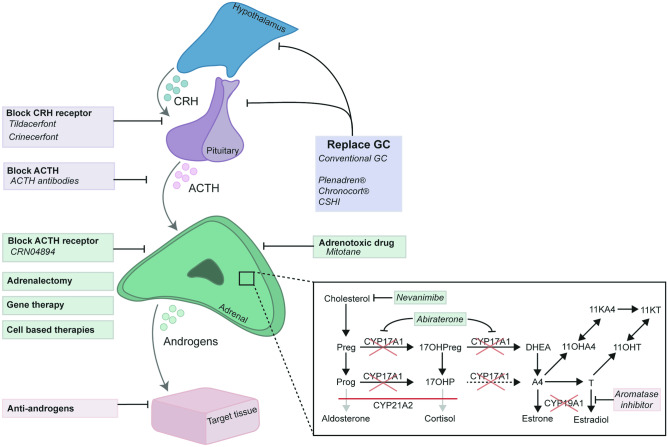
Fig. 1.
Novel therapeutic approaches for patients with 21OHD include the replacement of glucocorticoids (GC) by improved modified-release HC preparations (Plenadren®, Chronocort®) or improved modes of GC delivery (CSHI), associated with more efficient suppression of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA)-axis driven adrenal androgen production. This HPA-axis-driven adrenal androgen production may be additionally blocked by corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) receptor blocking (Tildacerfont, crinecerfont) or ACTH (receptor) blocking. Alternatively, adrenal androgen production may be inhibited by adrenal steroidogenesis blockers (Nevanimibe, abiraterone acetetate), adrenotoxic drugs (mitotane), or bilateral adrenalectomy. Inhibition of the aromatization of adrenal androgens may lower the suppressing effects of estrogens on growth and (co)-administration of anti-androgens may inhibit hyperandrogenic effects. Gene and cell-based therapies anticipate restoring the HPA-axis regulated glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid production