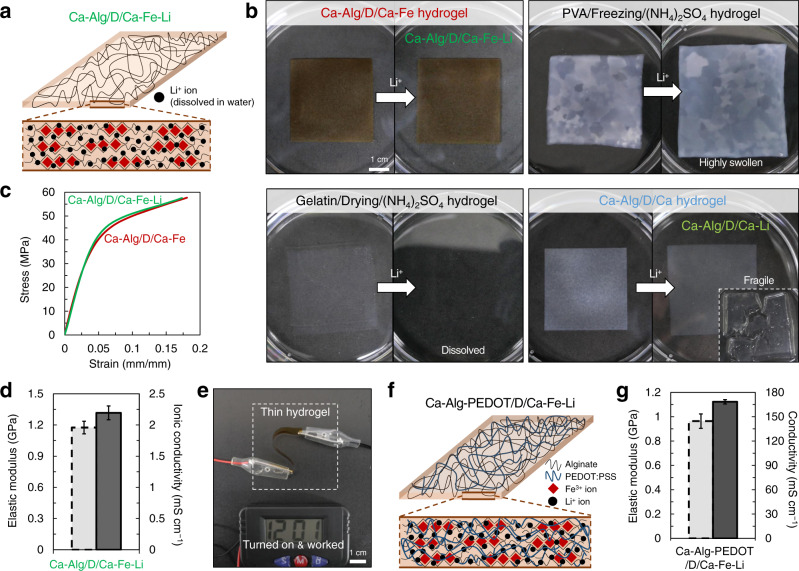
Fig. 4. Mechanically robust, conductive hydrogels applicable as a gel electrolyte.
a Illustration of Ca–Alg/D/Ca–Fe–Li hydrogel for electrolyte. b Photograph showing the fabrication of Ca–Alg/D/Ca–Fe–Li hydrogel and its stability in Li+ solution, and low mechanical stability of other hydrogels (PVA, gelatin, and Ca–Alg/D/Ca) in Li+ solution. c Stress–strain curves for Ca–Alg/D/Ca–Fe hydrogel before and after being soaked in Li+ solution. d Elastic modulus and ionic conductivity of Ca–Alg/D/Ca–Fe–Li hydrogel. e Photograph showing stable working performance of the Ca–Alg/D/Ca–Fe–Li hydrogel as a solid gel electrolyte. f Illustration of PEDOT-contained reconstructed hydrogel, Ca–Alg-PEDOT/D/Ca–Fe–Li. g Elastic modulus and conductivity of Ca–Alg-PEDOT/D/Ca–Fe–Li hydrogel. Error bars correspond to standard deviations.