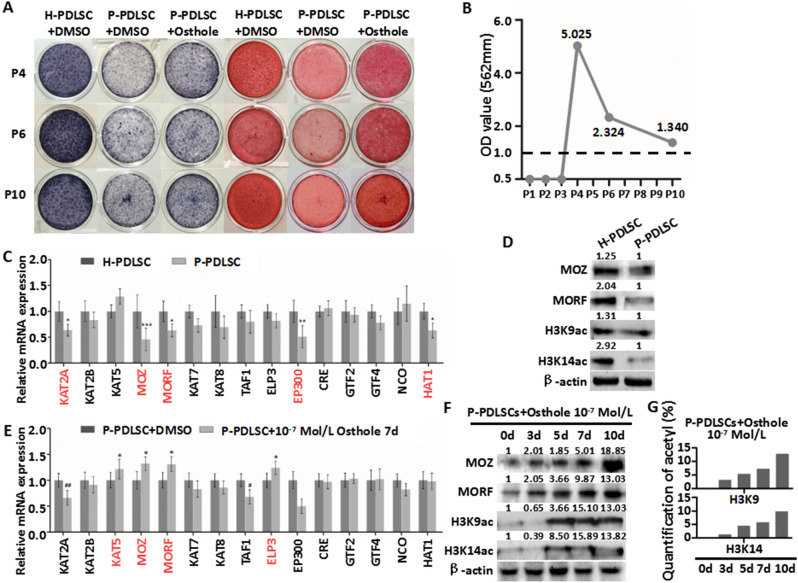
Figure 2.
Osthole reverses defective osteogenesis of P-PDLSCs through histone acetylation. (A) ALP staining and ARS staining of H-PDLSCs, P-PDLSCs and P-PDLSCs with 10−7 Mol/L Ostholes in P4 (with stimulation), P6 (without stimulation) and P10 (without stimulation). (B) Quantification of ARS staining for light absorbance at 562 nm. (C) qRT-PCR showed gene expression of fifteen histone acetylases in H-PDLSCs and P-PDLSCs. (D) Protein expression of MOZ, MORF, H3K9ac and H3K14ac in H-PDLSCs and P-PDLSCs as assayed by western blot. (E) qRT-PCR showed gene expression of fifteen histone acetylases in P-PDLSCs and P-PDLSCs with 10−7 Mol/L Osthole measured by qRT-PCR. (F) Protein expression of MOZ, MORF, H3K9ac and H3K14ac in P-PDLSCs with 10−7 Mol/L Osthole treatment on day 0, 3, 5, 7, 10 as assayed by western blot. (G) Level of acetylation of H3K9 and H3K14 in P-PDLSCs with 10−7 Mol/L Osthole treatment on day 0, 3, 5, 7, 10 as assayed by EpiQuik Global Acetyl Histone Quantification Kit. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, no mark: P ≧ 0.05, n = 3.