Figure 4. DDX5-dependent tuft cell gene programs in the small intestine.
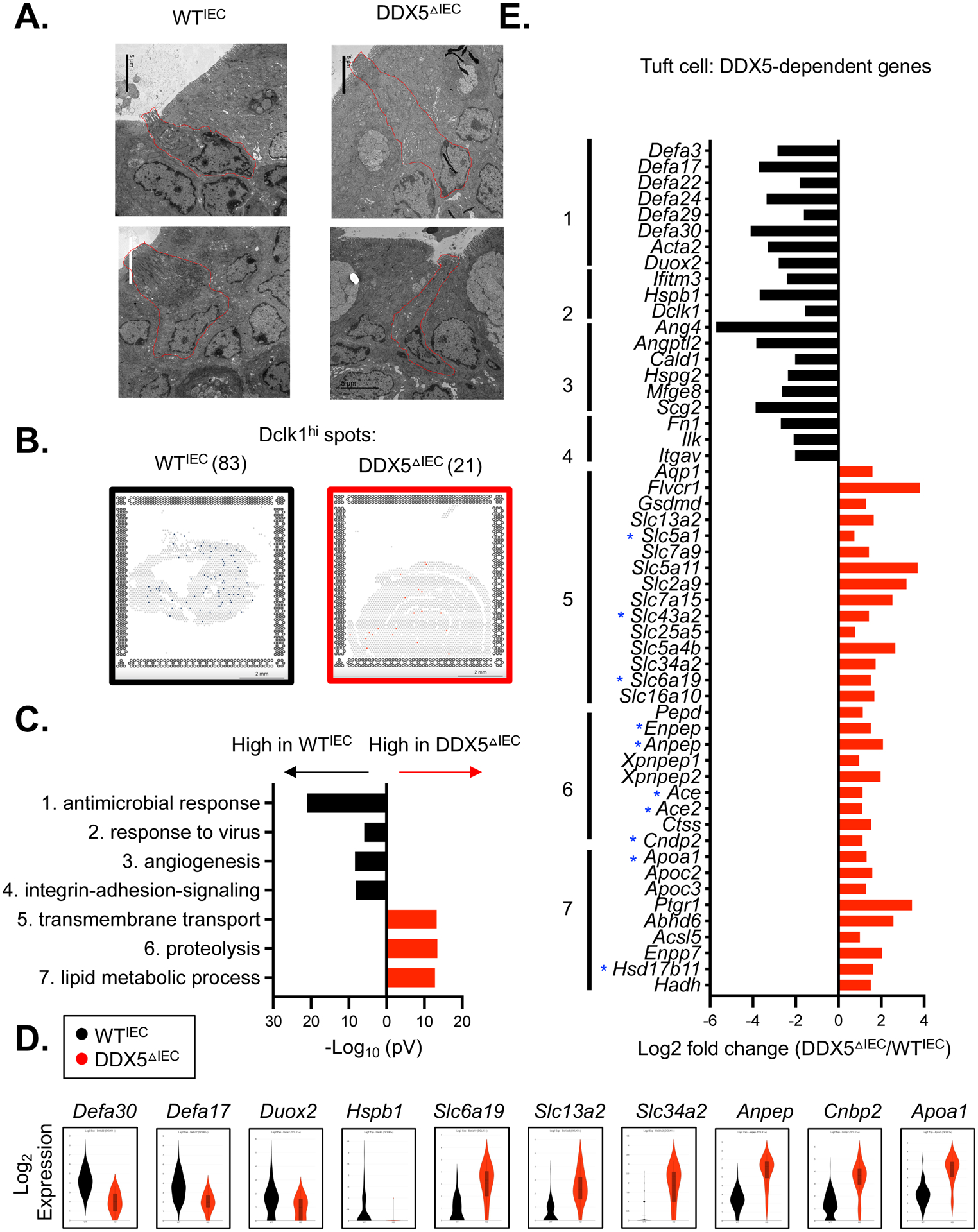
A. Representative electron microscopy images of small intestinal tuft cells from WTIEC and DDX5ΔIEC mice. Scale bar: 5μm.
B. Loupe browser screenshots displaying quantified Dclk1hi spots on the small intestinal sections from WTIEC and DDX5ΔIEC mice described in Figure 2A. Scale bar: 2mm.
C. Gene ontology analysis revealed the top 7 pathways downregulated (black) or upregulated (red) in DDX5ΔIEC Dclk1hi cells from B.
D. Violin plots displaying expressions of DDX5-dependent genes—with or without DDX5-associated transcripts—involved in the antimicrobial response (Defa3 and Defa17), viral response (Duox2 and Hspb1), transport (Slc6a19), proteolysis (Anpep and Cnbp2), or lipid metabolism (Apoa1) in WTIEC and DDX5ΔIEC Dclk1hi cells from C.
E. Log fold changes (DDX5ΔIEC/ WTIEC) in the expression of tuft cell DDX5-dependent genes participating in pathways identified in C. Small intestinal IEC DDX5-associated transcripts identified in eCLIP analysis are indicated with a blue star (GSE124023).
