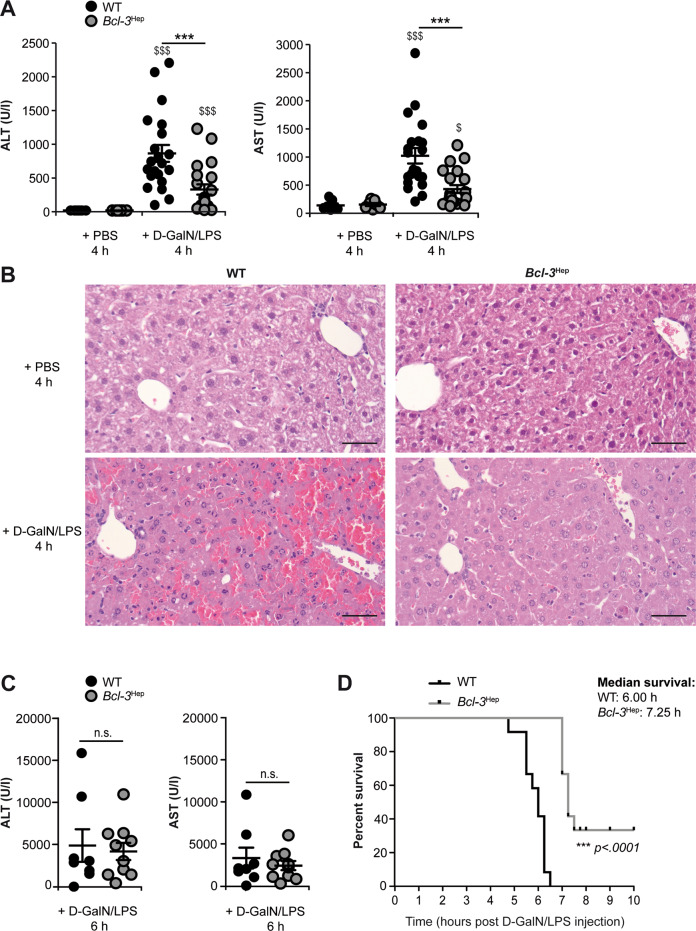
Fig. 1. Conditional overexpression of Bcl-3 in hepatocytes mitigated liver injury from d-GalN/LPS and promoted survival of mice.
Liver injury following treatment with d-GalN/LPS was assessed by measurement of A serum alanine and aspartate aminotransferase (ALT and AST) levels, and B standard H&E staining of liver sections (scale bar: 50 µm, representative histological photomicrographs) in Bcl-3Hep and WT mice at 4 h. C Serum transaminases in Bcl-3Hep and WT mice at 6 h post d-GalN/LPS. D Kaplan–Meier survival plots for Bcl-3Hep and WT mice after d-GalN/LPS injection. Data in A represent means ± SEM from four experiments with a total of n = 21 WT + d-GalN/LPS, n = 21 Bcl-3Hep + d-GalN/LPS, n = 7 WT + PBS and n = 7 Bcl-3Hep + PBS. Data in C represent means ± SEM of n = 10 mice/group, whereby 20% of the WT + d-GalN/LPS group was already dead at this time point. In D survival rate was monitored for 8 h after injection of d-GalN/LPS in a total of n = 12 WT and n = 10 Bcl-3Hep mice. ***p < 0.001 for WT vs. Bcl-3Hep and $p < 0.05, $$$p < 0.001 for PBS vs. d-GalN/LPS using Mann–Whitney U test (A and C) or a log-rank test (D). In C there was no statistical difference between the two groups in respect of the parameters.