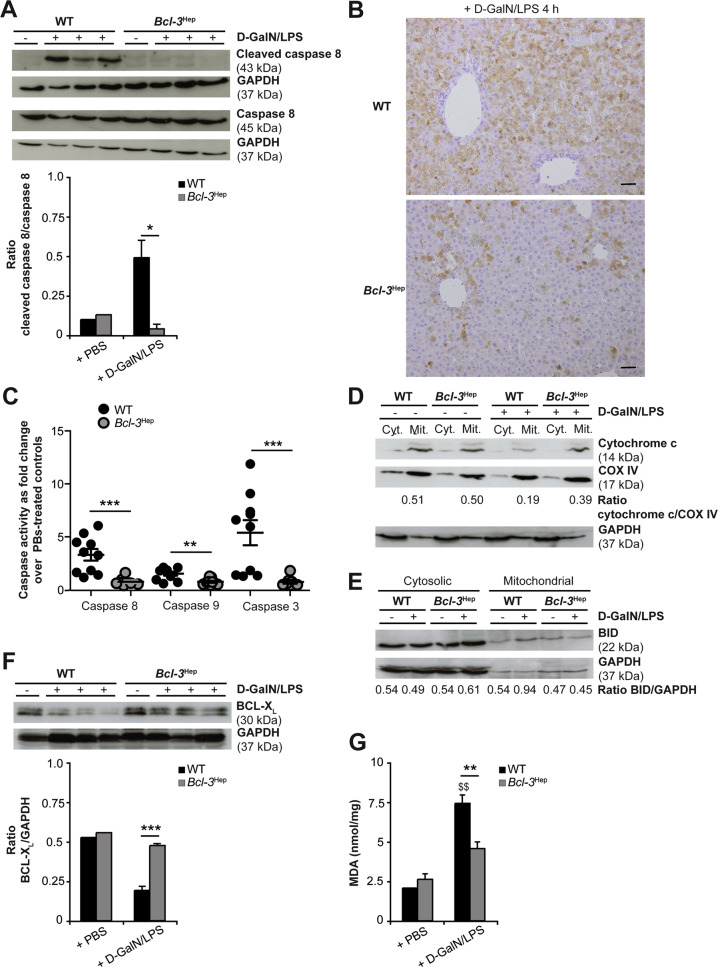
Fig. 2. Hepatoprotection in Bcl-3Hep mice against d-GalN/LPS is associated with a reduction of caspase activation, BCL-XL degradation and mitochondrial ROS formation.
Liver tissue of d-GalN/LPS-challenged Bcl-3Hep and WT mice was harvested after 4 h for immunodetection of A activated caspase 8 by immunoblotting, B activated caspase 3 by immunhistochemical staining, and C activated caspase 8, 9, and 3 by caspase enzyme assays (means of n = 10 mice/group ± SEM). Activation of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway was further evaluated by immunoblotting of D cytochrome c and E BID in cytosolic (cyt.) and mitochondrial (mit.) protein fractions, F BCL-XL in whole liver tissue lysates, and G determination of MDA content (means of n = 10 WT + d-GalN/LPS, n = 6 Bcl-3Hep + d-GalN/LPS, n = 2 PBS-treated controls per genotype ± SEM). In A and D–F representative immunoblots with densitometric analysis are shown. GAPDH and COX IV served as protein loading controls. In B representative histological photomicrographs (scale bar: 2000 µM) are depicted. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 for WT vs. Bcl-3Hep and $$ p < 0.01 for PBS vs. d-GalN/LPS using unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test (A, F, and G) or Mann–Whitney U test (C).