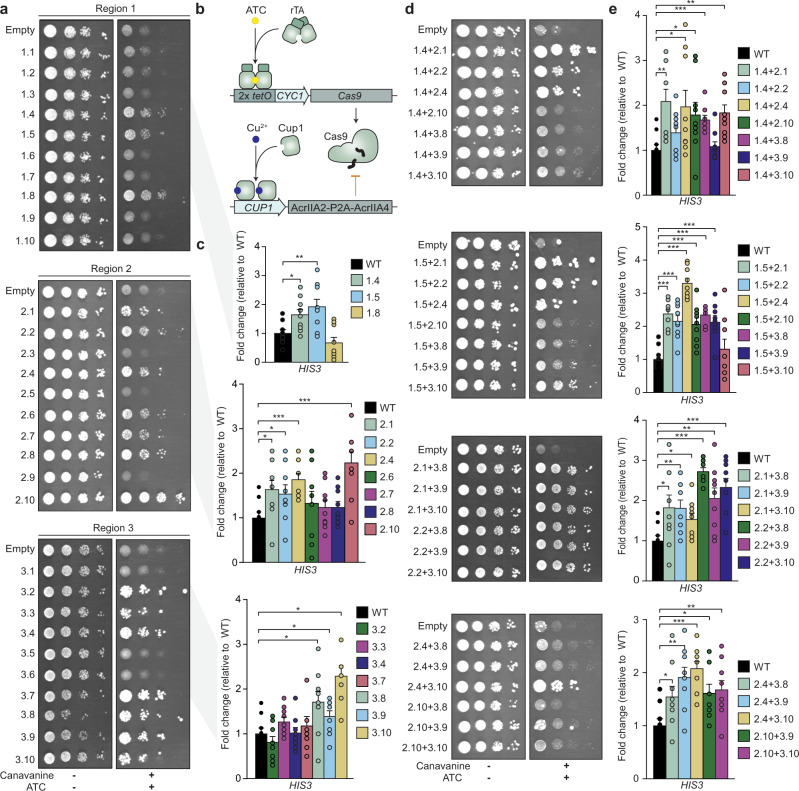
Fig. 2. Qualitative and quantitative screening of hyperactive Cas9 enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
a Yeast survival assays examining the functionality of individual Cas9 designs targeting CAN1 via survival on canavanine. b Schematic representation of the quantitative Cas9 inhibitor-modulated genetic circuit. c Quantitation of engineered Cas9 activity via yeast survival with the Cas9 inhibitor system and a gRNA targeting HIS3. d Survival assays to determine the functionality of engineered Cas9 enzymes combining multiple designed regions. e Quantification of the activities of combined Cas9 designs. Error bars: s.e.m. of n = 9 biologically independent replicates. A standard Student’s t-test with a two-tailed distribution and unequal variance assumed between samples was used to calculate the significance. p-values: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Specific p-values for panel c design vs WT: 1.4 p = 0.01, 1.5 p = 0.008, 2.1 p =0.02, 2.2 p = 0.05, 2.4 p = 0.0003, 2.10 p = 0.0007, 3.8 p = 0.02, 3.9 p = 0.05 and 3.10 p =0.0006 (Student’s t-test). Specific p-values for panel d design vs WT: 1.4 + 2.1 p = 0.004, 1.4 + 2.4 p = 0.03, 1.4 + 2.10 p = 0.03, 1.4 + 3.8 p = 0.001, 1.4 + 3.10 p = 0.002, 1.5 + 2.1 p = 1.4e-06, 1.5 + 2.2 p = 8.2e-05, 1.5 + 2.4 p = 4.9e-09, 1.5 + 2.10 p = 6.2e-04, 1.5 + 3.8 p = 6.7e-07, 1.5 + 3.9 p = 1.4e-04, 2.1 + 3.8 0.04, 2.1 + 3.9 p = 0.005, 2.1 + 3.10 p = 0.02, 2.2 + 3.8 p = 2.5e-08, 2.2 + 3.9 p = 0.004, 2.2 + 3.10 p = 0.0002, 2.4 + 3.8 p = 0.04, 2.4 + 3.9 p = 0.001, 2.4 + 3.10 p = 3.2e-05, 2.10 + 3.9 p = 0.01 and 2.10 + 3.10 p = 0.009 (Student’s t-test). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.