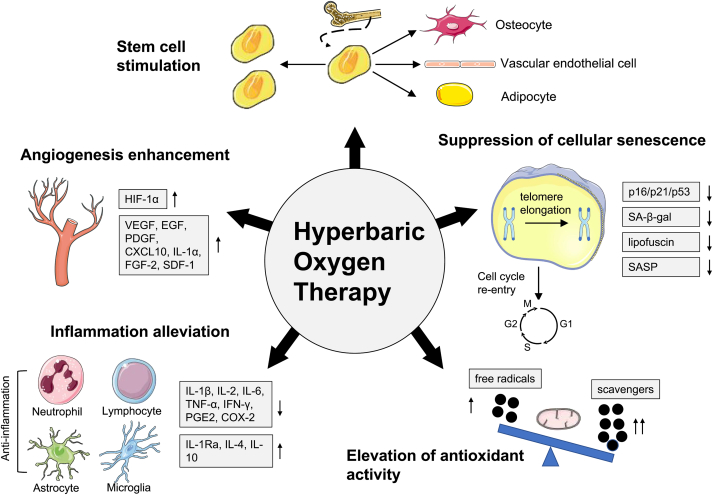
Fig. 3.
The mechanisms by which HBOT promotes healthy aging. HBOT can cause a wide range of cellular, biochemical and physiological changes. The proven biological mechanisms by which HBOT may promote healthy aging can be summarized into five categories. (1) HBOT enhances angiogenesis mainly by increasing the expression of HIF-1α and a series of angiogenic markers. (2) HBOT reduces inflammation by regulating the number and activity of extensive inflammatory cell types such as neutrophils, lymphocytes, astrocytes and microglia. At the molecular level, HBOT can inhibit pro-inflammatory factors while promoting anti-inflammatory factors. (3) HBOT enhances antioxidant defenses by modulating the balance between free radicals and scavengers. The process is closely correlated with the regulation of mitochondrial function. (4) HBOT interferes with the detrimental effects of cellular senescence, manifested by cell cycle re-entry and attenuation of senescence markers such as p16/p21/p53, SA-β-gal, lipofuscin and the SASP. HBOT also plays a role in inhibiting telomere shortening, one of the major stimuli of cellular senescence. (5) HBOT increases the number of circulating stem cells by stimulating stem cell mobilization, and changes stem cell properties by promoting proliferation and differentiation.