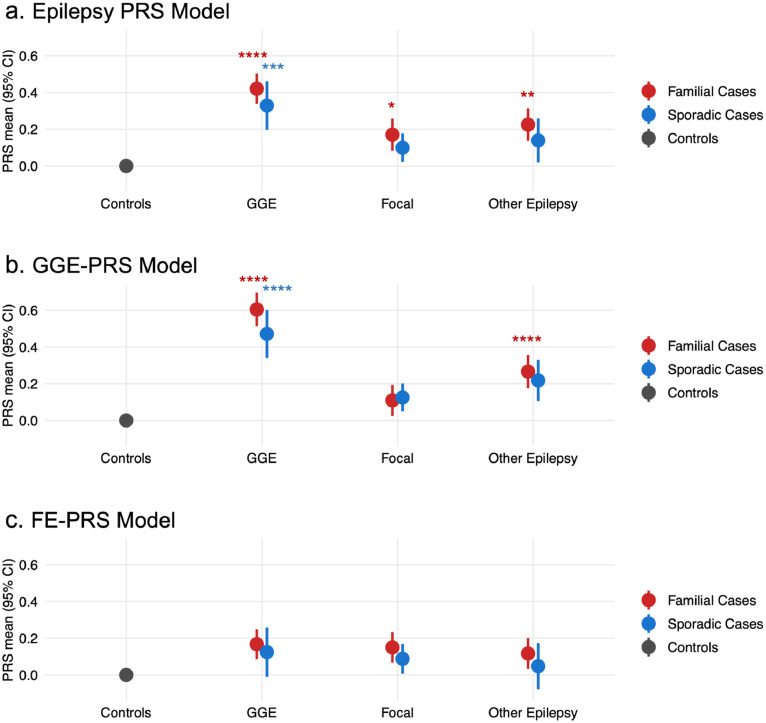
Figure 3.
Polygenic risk stratified by epilepsy type.
(a) The Epilepsy PRS model was highest in familial cases across all epilepsy phenotype groups. (b) The polygenic risk scores (PRS) model for risk of genetic generalised epilepsy (GGE) was highest in individuals with familial GGE. (c) The PRS model for risk of focal epilepsy was not different from controls in any of the phenotypic groups. Logistic mixed-effects regression models used PRS as exposure variable, sex and the first five ancestry principal components as fixed-effects covariates, and genetic relatedness matrix as random-effects covariate. Stars indicate statistically significant comparisons to the control group, corrected for multiple comparisons (* Padj ≤ 0.05, ** Padj ≤ 0.01, *** Padj ≤ 0.001, **** Padj ≤ 0.0001); all other comparisons were non-significant (Padj > 0.05). Full results are available in Supplementary Table 7.