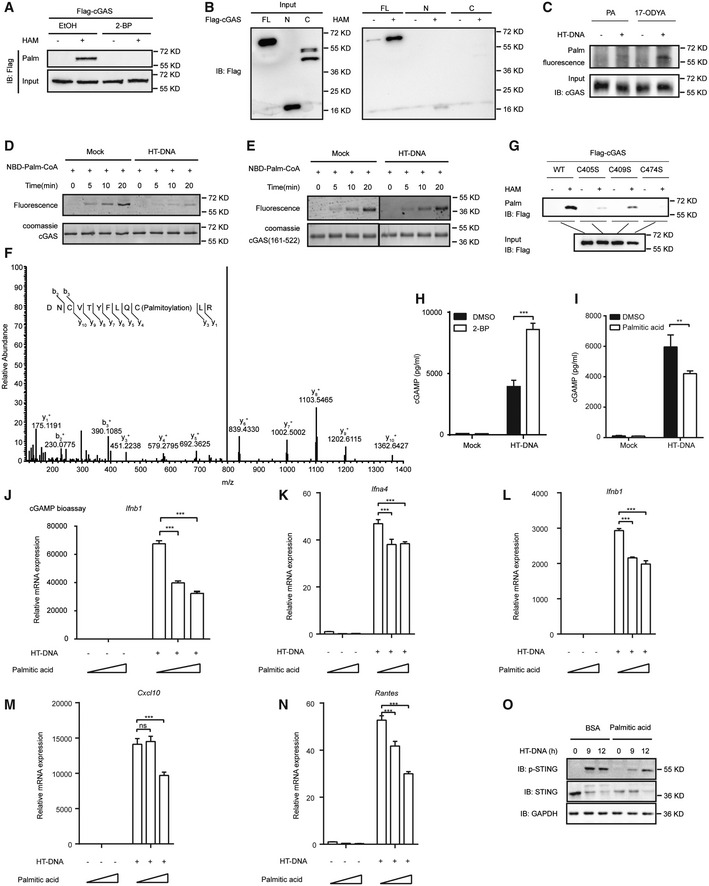
Figure 1. Palmitoylation of cGAS suppresses its activation.
-
AAcyl‐RAC assay of HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h.
-
BAcyl‐RAC assay of HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h.
-
CClick chemistry was applied to detect endogenous cGAS palmitoylation in RAW264.7 cells.
-
D, EIn vitro palmitoylation assay for the indicated proteins. NBD‐Palm‐CoA: (N‐[(7‐nitro‐2‐1,3‐benzoxadiazol‐4‐yl)‐methyl] amino) palmitoyl‐CoA. The recombinant cGAS protein used in the assay was indicated by Coomassie blue staining.
-
FLC‐MS/MS analysis of palmitoylated peptides of cGAS.
-
GAcyl‐RAC assay of HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h.
-
H, ITHP‐1 cells were treated with DMSO or 2‐BP (50 μM) (H) or palmitic acid (100 μM) (I) for 12 h. Six hours after transfection with HT‐DNA (2 μg/ml), cGAMP was extracted and quantified by cGAMP ELISA.
-
JTHP‐1 cells were treated with palmitic acid (0, 50, or 100 μM) for 12 h before a cGAMP bioassay.
-
K–NBMDMs were treated with palmitic acid (0, 100, or 200 μM) for 12 h and transfected with HT‐DNA (2 μg/ml) for 6 h before RT–qPCR analysis of Ifna4 (K), Ifnb1 (L), Cxcl10 (M), and Rantes (N) expression.
-
OL929 cells were treated with BSA and palmitic acid (100 μM) and transfected with HT‐DNA (2 μg/ml) for the indicated times before immunoblotting analysis with the indicated antibodies.
Data information: 17‐ODYA, 17‐octadecanoic acid; 2‐BP, 2‐bromopalmitate; C, C‐terminal domain; EtOH, ethanol; FL, full length; HAM, hydroxylamine; N, N‐terminal domain; PA, palmitic acid. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Mean ± SEM from triplicates of technical replicates, unpaired t‐test; ns, not significant; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.001 (H–N).
Source data are available online for this figure.
