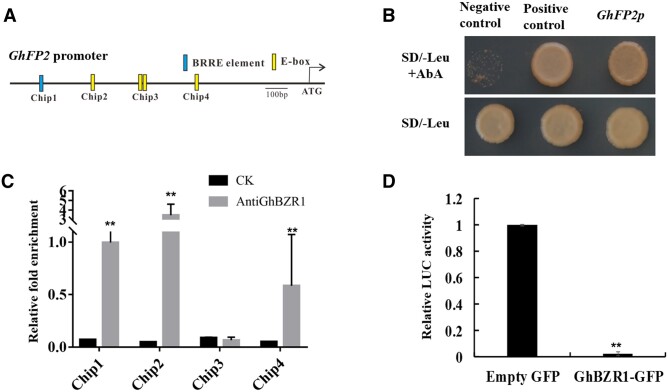
Figure 1.
Promoter activity of GhFP2 is suppressed by GhBZR1. A, The potential BRRE and E-box elements in GhFP2 promoter sequence. BRRE (CGTGT/CG), E-box (CANNTG). B, Y1H assay of GhBZR1 interaction with GhFP2 promoter sequence. Transformants grew on SD/–Leu nutritional selection medium with 350 ng/ml Aureobasidin A (AbA). Y1H Gold yeast transformants of pGADT7-Rec-p53/p53-AbAi and pGADT7/GhFP2p-pAbAi were used as the positive and negative controls, respectively. C, ChIP-qPCR) assay of the GhBZR1-binding cis-motifs in promoter of GhFP2 in vivo. GhBZR1-bound chromatin DNA fragments were isolated from nine DPA fibers of WT cotton, and qPCR analysis was performed with the primer sets listed in Supplemental Table S3 (see “Materials and methods”). CK, the control sample without anti-GhBZR1 antibody. D, Dual-LUC assay of transcriptional repression of GhBZR1 to GhFP2. GhFP2 promoter was fused to the LUC reporter, and the promoter activity was determined by relative luciferase activity assay in leaves of N. benthamiana. The relative LUC activity was normalized to the reference REN luciferase. The effector GhBZR1 and empty vector were co-filtrated with reporter ProGhFP2:Luc, respectively, and the relative LUC activity with empty vector was set as 1. Data in C were analyzed with prism7.0. Data in D were analyzed with Microsoft Excel. Error bars represent the sd. Mean values and sd are shown from three biological replicates. Independent t tests demonstrated significant (P < 0.05) or very significant (P < 0.01) difference between two groups.