Fig. 4.
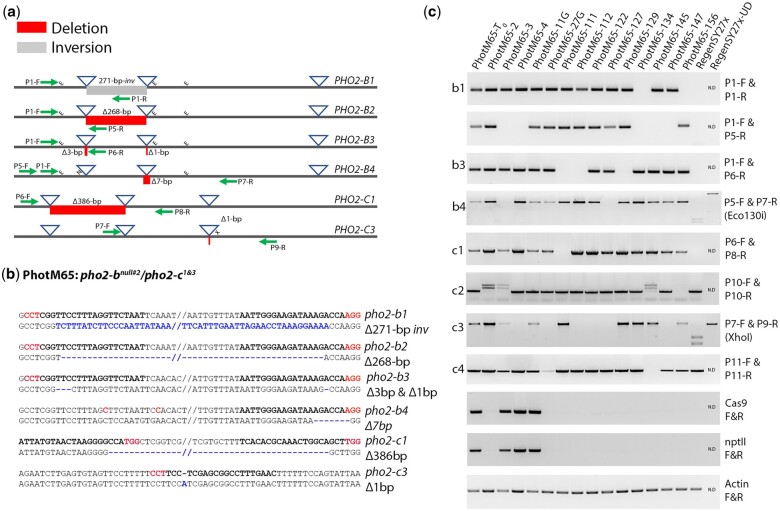
The validation PhotM65 mutant plants. a) Schematic representation of the PCR assays used to validate mutant haplotypes. The blue triangle represents the reagent target sites and the red and gray boxes indicate deleted or inverted DNA sequences, respectively. The green arrows represent the approximate primer locations used to generate amplicons. The “E,” “X,” and the “NlaIV” indicate the location of the Eco130i, XhoI, and NlaIV restriction sites used to genotype haplotypes. b) Sequence confirmation of the haplotypes was carried out using sequence data from the LAA analysis as well as from cloning and sequencing assays using haplotype specific amplicons. The bold red and black text represents the PAM and target guide RNA sites for each reagent, respectively, and the blue text and lime green highlights indicate inverted or deleted DNA sequence. c) Gel images of mutant and wild-type haplotype-specific amplicons from PhotM65 T0 and T1 plants. The absence of a haplotype specific amplicon indicates the segregation of the mutant haplotype in respective plants. Amplicons for the Cas9 and the nptII selectable marker were used to identify the presence or absence of reagent T-DNA in the mutant plants.