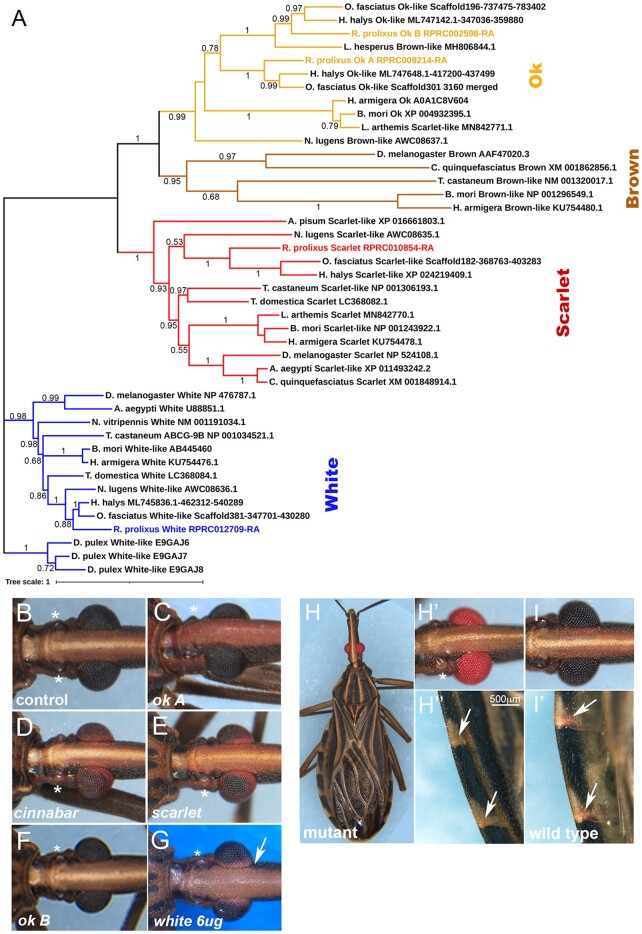
Fig. 4.
Eye color phenotypes resulting from the KD of genes involved in pigment production and transport. a) Phylogenetic analysis of R. prolixus ABC pigment transporters. The ABCs evolutionary history was inferred by the Maximum Likelihood method followed by 500 bootstrap replicates. Bootstrap values are displayed in nodes. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured as the number of substitutions per site. This analysis involved 43 amino acid sequences. Adult eye color phenotypes observed following fifth instar dsRNA injections for b) control; c) ok A; d) cinnabar; e) scarlet; f) ok B; and g) white. h) Spontaneous R. prolixus red eye mutant. h′) Detail of the mutant eye and ocelli, compared to the i) wild-type. Note the absence of ocelli pigmentation (asterisk). h″) Detail of mutant abdominal connexives, with loss of red pigment in veins, present as red spots in the i′) wild-type (arrows).