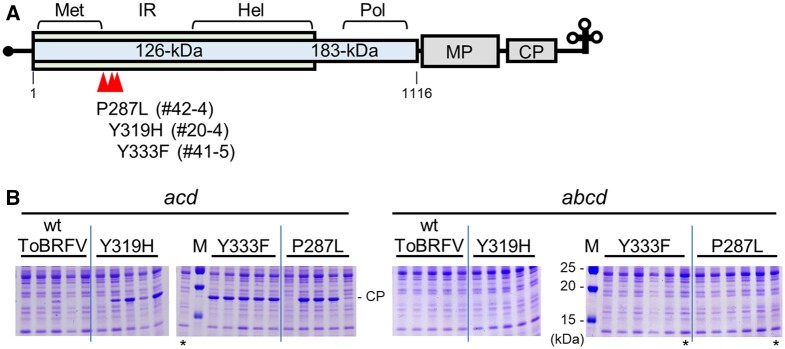
Figure 4.
ToBRFV mutants with increased infectivity to Sltom1acd triple-mutant plants. A, Mutation sites in the ToBRFV genome. Boxes represent the coding regions for the 126-kDa and 183-kDa replication proteins, movement protein (MP), and CP. Regions for methyltransferase-like (Met), helicase-like (Hel), and polymerase-like (Pol) domains, and intervening region of the replication proteins are shown. Amino acid changes from original ToBRFV to the mutants are shown along with the ID numbers of plants from which the mutant ToBRFV was recovered. B, ToBRFV CP accumulation in Sltom1 quadruple- (abcd) and Sltom1acd triple- (acd) mutant plants. Tomato plants were cotyledon-inoculated with leaf homogenates that were prepared from N. benthamiana leaves to which capped RNA synthesized from wt or mutant ToBRFV infectious clone plasmids had been inoculated. Upper uninoculated leaves were harvested at 21 dpi (Sltom1acd) or 20 dpi (Sltom1abcd) and CP accumulation was examined and presented as described in Figure 2A. Only the relevant parts of the gels with the CP bands are shown in this figure and whole gel images are provided in Supplemental Figure S7.