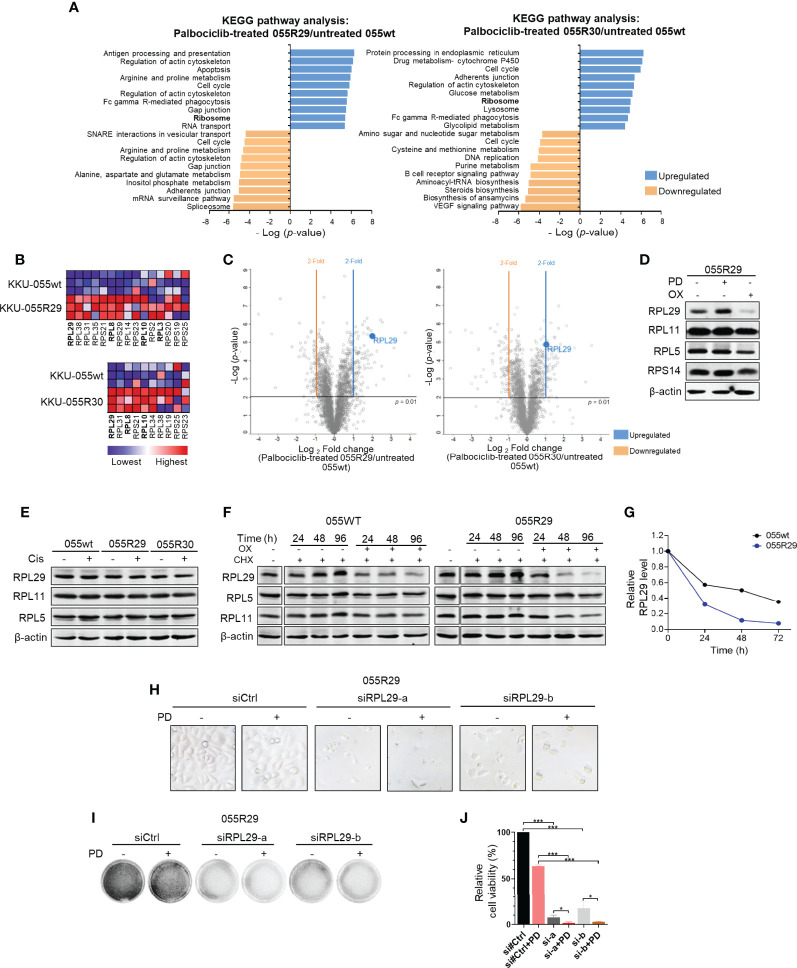
Figure 3.
Dysregulated expression of specific ribosomal protein in CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant CCA cells. (A) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichments in palbociclib-treated KKU-055R29 (left) and KKU-055R30 (right) compared to untreated KKU-055wt. (B) Ribosome gene set enrichment shows significant ribosomal protein enrichment in palbociclib-treated KKU-055R29 and KKU-055R30 compared to untreated KKU-055wt (p<0.05). The heat map shows the enrichments in triplicate (highest in red, lowest in blue). Ribosomal proteins in the RPL29 complex are shown in bold. (C) Volcano plots of protein expressions in palbociclib-treated KKU-055R29 (left) and KKU-055R30 (right) compared to untreated KKU-055wt. (D) Western blot analysis of ribosomal proteins in KKU-055-resistant clone R29 after 24 hours of treatment with 1 µM palbociclib, 5 µM oxaliplatin, or vehicle. β-Actin was used as the loading control. (E) Western blot analysis of ribosomal proteins in KKU-055wt and KKU-055-resistant clones after 24 hours of treatment with 0.5 µM cisplatin or vehicle. (F) Western blot analysis of ribosomal proteins in KKU-055-resistant clone R29 (right) after 24-, 48-, and 96-hours of treatment with vehicle, 0.5 µM cycloheximide, or 0.5 µM cycloheximide combined with 5 µM oxaliplatin. (G) Quantitation of RPL29 half-life in KKU-055wt compared to that of KKU-055R. At each time point, the protein amount was quantitated and normalized relative to β-actin. (H) Phase-contrast images of KKU-055-resistant clone R29 treated with non-targeting siRNA (siCtrl) or RPL29 siRNAs (siRPL29-a, siRPL29-b) for 48 hours, and then treated with 0.5 uM palbociclib (PD) or vehicle for 72 hours. (I) Images of crystal violet staining from H. (J) Relative survival from F was quantified. The bars represent the average of 3 replicates ± standard deviation (SD). Analysis for statistical significance was performed using Student’s t-test (*p≤0.05, and ***p≤0.001).