Fig. 2.
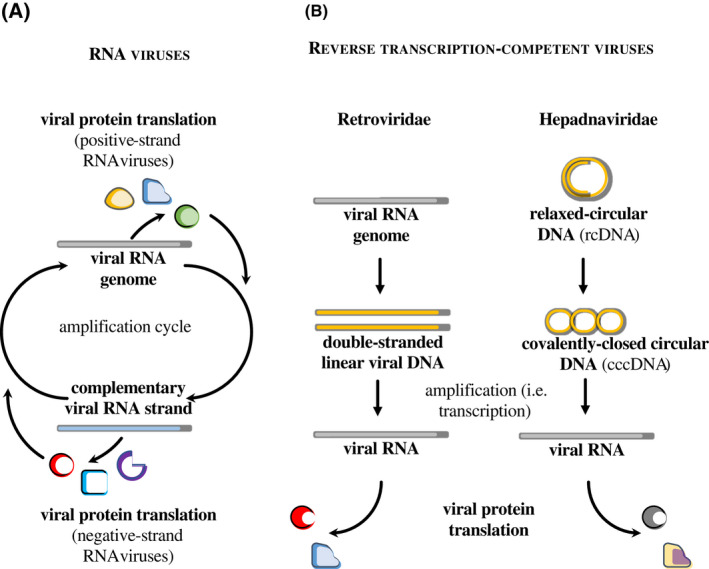
Strategies for viral genome amplification used by viruses reported to be inhibited by ISG20. (A) Simplified overview of the RNA amplification cycle used by positive‐ and negative‐strand RNA viruses. Upon entry, the RNA genome of positive‐strand RNA viruses is translated into viral proteins that promote synthesis of the complementary RNA strand and ensure the amplification cycle. In the case of the latter instead, a first round of pioneer RNA synthesis is needed to ensure the first round of viral protein translation. (B) Schematic overview of the strategy used by Retroviridae and Hepadnaviridae to replicate through an intermediate reverse transcription step. In this case, viral RNA is amplified through transcription of RNAs of positive polarity in the cell nucleus, a process that co‐opts the cellular RNA polymerase II.
