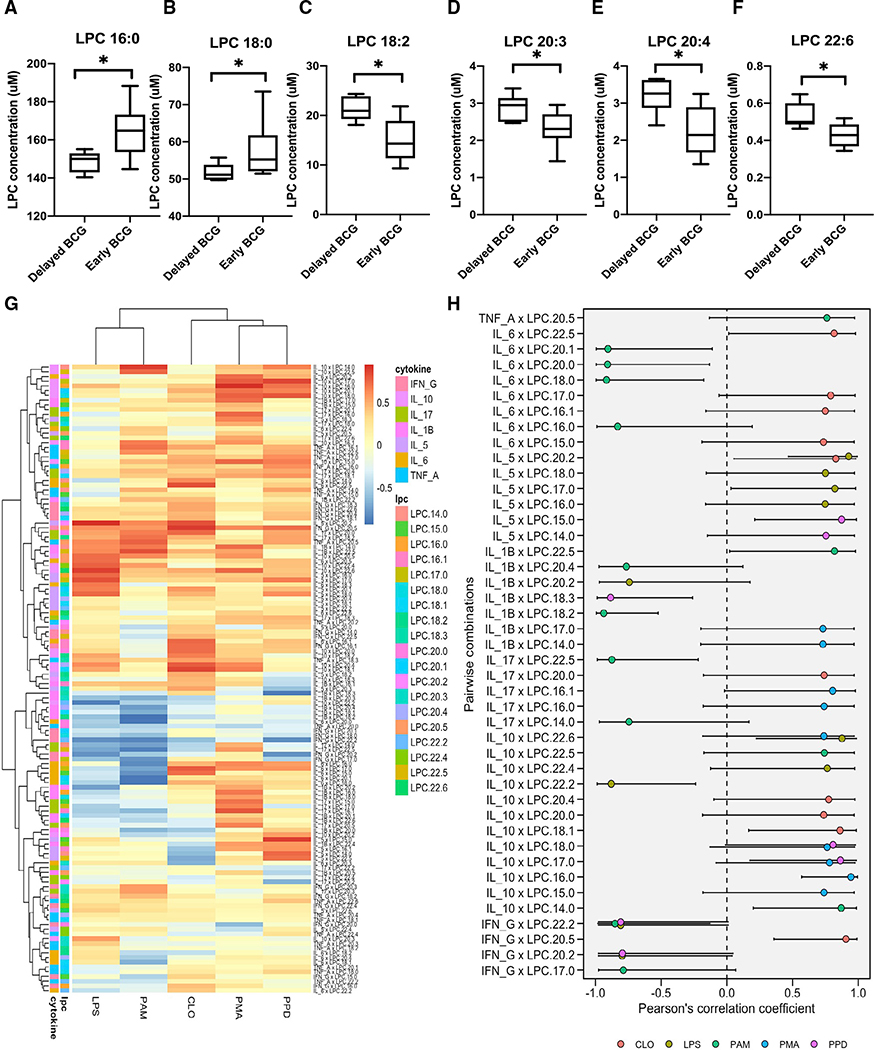
Figure 6. BCG-induced plasma lysophospholipids correlated with TLR- and mycobacterial antigen-induced cytokine responses.
Peripheral blood was collected from early versus delayed BCG immunized infants in Guinea-Bissau at 4 weeks of age and diluted for in vitro TLR agonist- and PPD-induced stimulation assay, as previously described (Jensen et al., 2015).
(A–F) Early administration of BCG was associated with perturbation of multiple LPCs as compared with delayed BCG. LPC concentrations are depicted as boxplots. Significance was calculated using the Mann-Whitney rank test between unpaired samples. *p < 0.05.
(G) Cytokines and chemokines were measured after multiple antigen recall responses of delayed and early BCG newborn samples. Response from PMA, LPS (TLR4 agonist), PAM3CSK4 (TLR 2/1 agonist), CLO75 (TLR 7/8), and PPD were correlated for corresponding matched samples using Pearson correlations of all LPCs. Data are presented as correlation estimates of cytokines/chemokines versus LPCs. These estimates were calculated from log2 fold-changes for early BCG versus delayed BCG.
(H) The summary correlation coefficient (R) from selected significant cytokine and LPC correlations is depicted on a forest plot. The plot presented significant correlations with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).