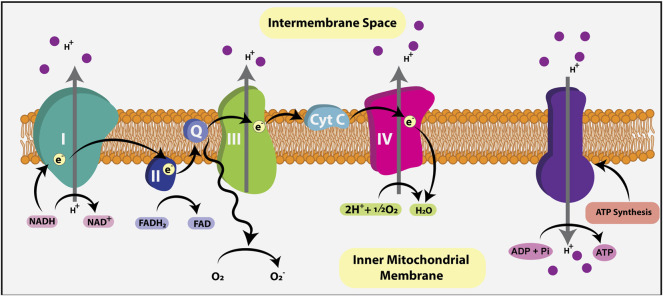
FIGURE 3.
Electron transport chain (ETC). The ETC generates ATP using the reducing agents NADH and FADH2, metabolic byproducts of the TCA cycle that donate electrons to the ETC. Electrons are shuttled through four transmembrane complex proteins (I-IV) in the IMM. NADH binds to complex I while FADH2 binds to complex II, initiating electron flow. The ETC uses electron transfer to pump a proton into the intermembrane space. This voltage gradient generates a proton motive force that drives O2-coupled ATP generation via ATP synthase, termed oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). OXPHOS generates ∼30–38 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose.