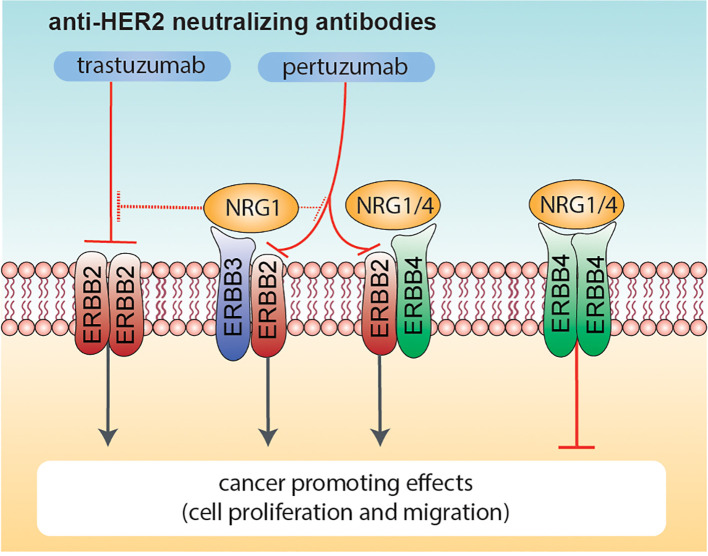
Figure 7.
Effects of combinatorial treatments with Neuregulins and anti-ERBB2 agents on breast cancer cell proliferation. Schematic diagram summarizing the effects induced by co-administration of anti-ERBB2 agents (trastuzumab and pertuzumab) and Neuregulins (NRG1 and NRG4) on breast cancer cell proliferation. NRG1 binds to ERBB3 and ERBB4, whereas NRG4 specifically binds to ERBB4. Neuregulin-activated ERBB3 and ERBB4 preferentially heterodimerize with ERBB2 (if available), in turn promoting cancer cell proliferation. Trastuzumab robustly inhibits ERBB2 ligand-independent activation as homo-dimer, whereas pertuzumab is more efficient in inhibiting HER2 hetero-dimerization with other ERBB receptors (including ERBB3 and/or ERBB4 activated by NRG1 or NRG4). NRG1 also reduces the efficacy of anti-HER2 agents, in particular trastuzumab. In contrast, the co-treatment of NRG4 and anti-HER2 agents promotes ERBB4 homodimers activation, in turn reducing breast cancer cell proliferation.