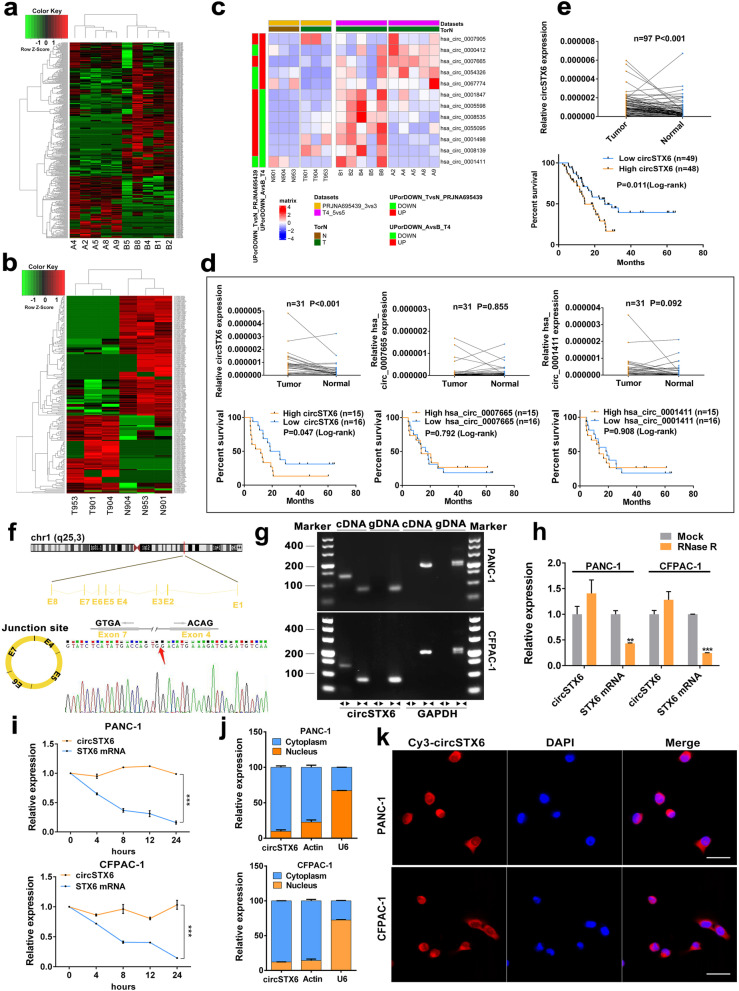
Fig. 1.
Identification and characterization of circSTX6 in PDAC cells and tissues. a Clustered heatmap of the differentially expressed circRNAs in PDAC tissues from five T4 PDAC patients with long survival time (Group B) and tissues from five T4 PDAC patients with short survival time (Group A). b Clustered heatmap of the differentially expressed circRNAs in three paired PDAC tissues (Group T) and matched noncancerous tissues (Group N). c Clustered heatmap of the intersection of two sequencing results. d Relative expression of three circRNA candidates (circSTX6, hsa_circ_0007665, hsa_circ_0001411) in 31 pairs of T4 PDAC tissues and corresponding noncancerous tissues. Kaplan–Meier analyses of the correlation between circRNA expression and overall survival were constructed. e Relative expression of circSTX6 in 97 pairs of PDAC tissues and corresponding noncancerous tissues. Kaplan–Meier analyses of the correlation between circSTX6 expression and overall survival were performed. f Schematic illustration of the genomic location and back splicing of circSTX6, with the splicing site validated by Sanger sequencing. g The existence of circSTX6 and STX6 were detected by qRT–PCR and agarose gel electrophoresis using divergent and convergent primers. h CircSTX6 and STX6 mRNA expression in PDAC cells were detected after RNase treatment compared to mock treatment. i. qRT–PCR analysis of circSTX6 and linear STX6 in PDAC cells treated with actinomycin D at the indicated time points. j Nuclear-cytoplasmic fractionation assay identified the localization of circSTX6. Actin and U6 were used as cytoplasmic and nuclear controls, respectively. k The subcellular location of circSTX6 in PDAC cells was investigated by FISH. Original magnification 400 ×. Scale bar = 50 μm. (Values are expressed as the means ± SDs; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001)