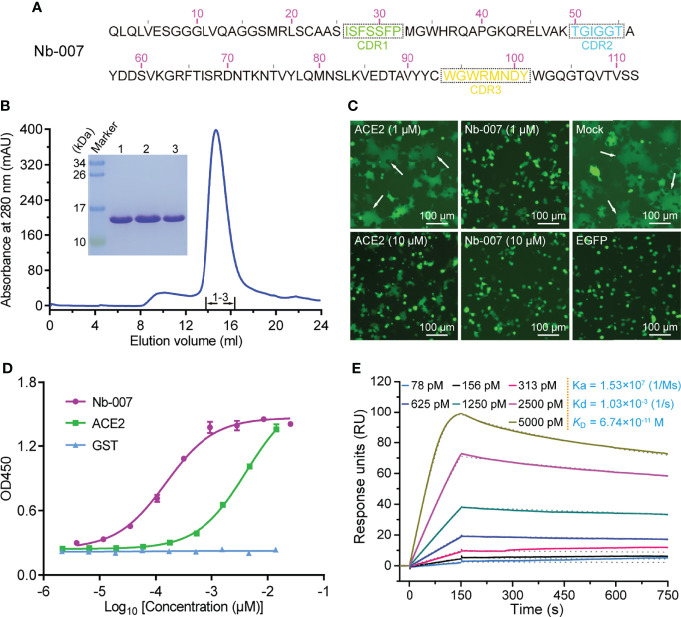
Figure 1.
Identification and functional characterization of Nb-007 as a neutralizing nanobody with high binding affinity towards SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD. (A) The amino-acid sequence of Nb-007. The three complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) are labelled with dashed boxes. (B) Characterization of the solution behavior of Nb-007 by gel filtration chromatography. The inset figure shows the SDS-PAGE analyses of the pooled samples. (C) Inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 S-protein-mediated syncytium-formation in the presence of Nb-007 or ACE2 at the indicated concentrations. Mock: cell-cell fusion induced by mixing HEK293T-ACE2 and HEK293T-S/EGFP cells without the addition of either the nanobody or ACE2. EGFP: only 293T-S/EGFP cells. The representative syncytia are marked with white arrows. Scale bar equals 100 µm. (D) The multi-concentration ELISA-binding profile between SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD and the indicated proteins (Nb-007, ACE2 and GST). The OD450 emissions are plotted as curves. Each error bar represents the mean ± SD from three independent experiences. (E) Interaction between Nb-007 and SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD detected via SPR. The recorded binding profiles and calculated kinetic parameters are shown.