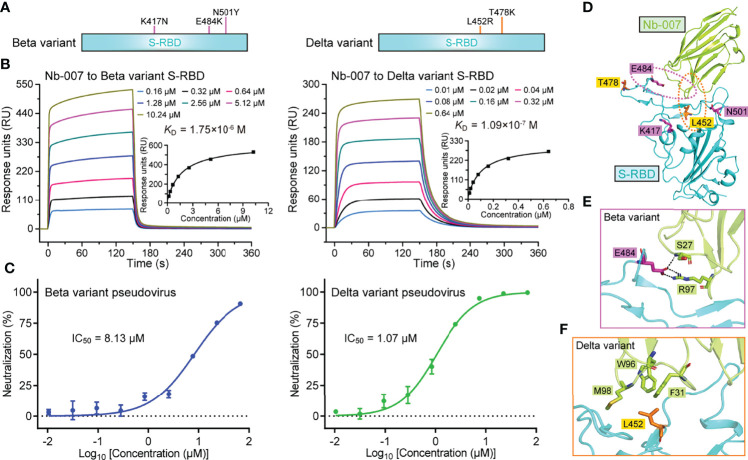
Figure 5.
Binding capacity and neutralizing activity of Nb-007 against SARS-CoV-2 variants. (A) Schematic view of the SARS-CoV-2 variants highlighting the mutations identified in S-RBD. Left panel: Beta variant. Right panel: Delta variant. (B) Affinity analysis of the binding of Nb-007 to the indicated SARS-CoV-2 variant S-RBD using SPR. The real-time binding kinetics are shown. (C) Inhibition of the pseudovirus entry by Nb-007 at the indicated concentrations for the SARS-CoV-2 variants. Each error bar represents the mean ± SD of triplicate. (D) An overview of the steric positions for those mutations identified in the SARS-CoV-2 variants relative to the bound nanobody. The three mutations in the Beta variant and two mutations in the Delta variant are shown as sticks and colored magenta and orange, respectively. Residues E484 and L452 are highlighted and their amino acid interaction details with the bound nanobody are further presented in (E, F), respectively. (E) The interactions between S-RBD E484 and Nb-007 S27 and R97. (F) The interactions between S-RBD L452 and Nb-007 F31, W96, and M98.