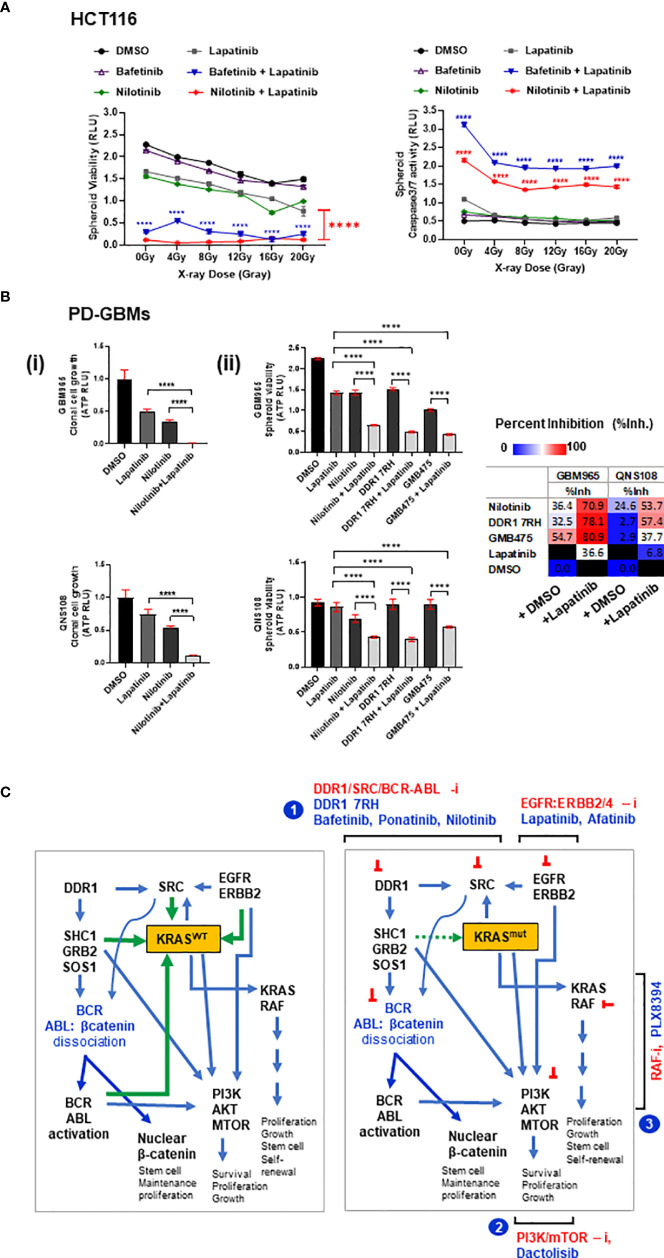
Figure 7.
(A) HCT116 multi-spheroids that recovered from radiation stress induced by administering IR doses from 0 up to 20 Gy were measured for (i) spheroid viability and (ii) caspase 3/7 activity at day 5 post-IR. p-Values for combination treatment of drugs (bafetinib or nilotinib) with lapatinib are marked with asterisks at each of the respective IR doses administered. (B) Combinatorial efficacy of nilotinib plus EGFR inhibitor lapatinib on spheroid formation and viability of patient-derived GBM (GBM-PD) lines GBM965 and QNS108. The intrinsic radiosensitivity of these lines is included in the Supplementary Methods. (C) Proposed model illustrating the signaling networks involving DDR1, SRC kinases, BCR-ABL-β-catenin, EGFR/ERBB2, KRAS, and PI3K/AKT proteins, and site of action of the leads identified. Illustration (left) shows KRASWT cross-talks: activated DDR1 relays its effect via adaptor proteins SHC1/GRB2/SOS1, causing dissociation of BCR-ABL-β-catenin complex (inactive), thereby activating BCR/ABL proteins. BCR and ABL proteins interact to cause activation of KRASWT and PIK3/AKT signaling axis. SRC kinase-activated downstream of DDR1 can engage with KRAS in a positive feedback loop. Additionally, EGFR/ERBB2 receptor complex can activate KRAS-dependent MAPK signaling and PIK3/AKT signaling; activated KRAS can also activate PI3K/AKT axis. Green arrows indicate input signals that activate KRASWT, and blue arrows indicate output signals from KRAS to other signaling intermediates. Illustration (right) depicts these signaling interactions with KRASmut protein, which is nearly constitutively active, thus independent of input signals. Targeting the network of hyperactivated KRAS or KRASmut comprises the following scheme: 1) combinatorial targeting of DDR1 and BCR-ABL1 by specific inhibitors of DDR1 or DDR1/BCR-ABL by multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (bafetinib, ponatinib, and nilotinib) in combination with EGFR inhibitors lapatinib and afatinib. Other potential combinations identified are represented as schemes (2) and (3): involving PI3K/mTOR inhibition by dactolisib, in combination with EGFR inhibitors lapatinib and afatinib or KRAS/RAF axis inhibition by PLX8394 in combination with EGFR inhibitors lapatinib and afatinib. These combinatorial schemes can be harnessed to overcome the treatment resistance observed in WNT-activated (stem-like) KRAS mutant tumors. Statistical significance is indicated as ****p < 0.0001.