Figure 3.
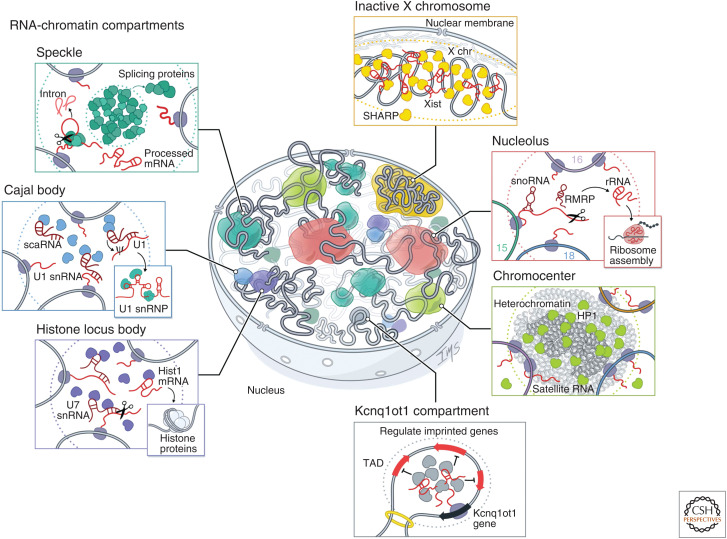
RNA-chromatin compartments regulate various processes throughout the nucleus. RNA has been shown to organize nuclear bodies involved in RNA processing, chromatin regulation, and gene expression. These include RNA processing bodies such as the nucleolus: The nucleolus is the site of ribosome biogenesis within the nucleus. Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) genes transcribed from multicopy genes on distinct chromosomes are positioned within nucleoli where they are transcribed by RNA Pol I. These nascent 45S pre-ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) are processed by small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs) and cleaved by RNAse P (RMRP) into mature 18S, 5.8S, and 28S rRNA and assembled into ribosomes. Histone locus bodies (HLBs): HLBs contain histone gene loci and are sites of histone pre-mRNA transcription and processing. The U7 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) cleaves the 3′ ends of histone pre-mRNAs to produce mature histone mRNAs. Cajal bodies: Cajal bodies are sites of snRNP maturation. Splicing snRNAs are transcribed from genes located at multiple sites across the genome and are modified by small Cajal body-associated RNAs (scaRNAs). Speckles: Nuclear speckles are nuclear bodies with high concentrations of pre-mRNA splicing proteins and snRNAs. Certain transcriptionally active genomic loci are positioned proximal to speckles. Other nuclear structures are associated with chromatin regulation and gene expression, such as the inactive X chromosome: The Xist long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) is responsible for chromosome-wide silencing, compaction, and localization of the inactive X chromosome to the nuclear lamina in female cells. It orchestrates silencing through direct binding and recruitment of the SHARP repressive protein to the X chromosome. Chromocenter: Satellite DNA repeats on multiple chromosomes are compacted into heterochromatin-dense foci. These foci are enriched for Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) and typically repressed, but satellite RNAs are also expressed at low levels and transcribed from these compartments. These RNAs are required for HP1 localization to chromocenters. Genomic imprinting: The Kcnq1ot1 lncRNA silences gene expression of imprinted target genes located in a 3D compartment next to its transcriptional locus. It does this by directly binding and recruiting the SHARP repressive protein to these target loci within a topologically associated domain (TAD), which results in silencing of gene expression.