Figure 4.
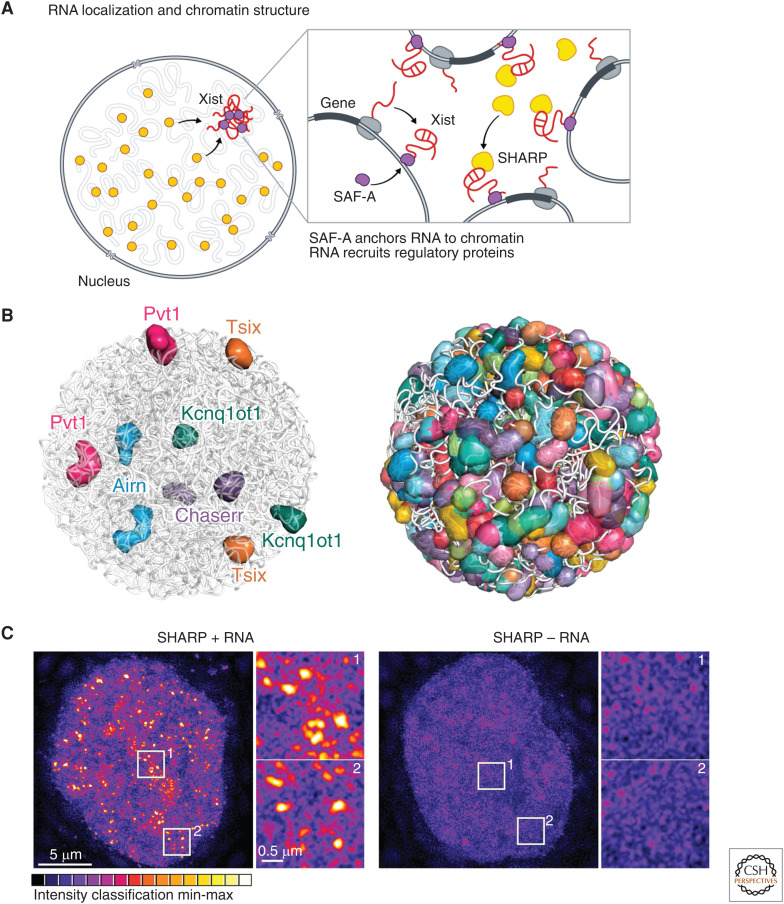
RNA localization and nuclear structure. (A) The Xist long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) acts in cis to silence transcription of the genes located proximal to its transcriptional locus. It is anchored to chromatin through interactions with the scaffold attachment factor A (SAF-A) DNA/RNA binding protein and, at these sites, directly binds to and recruits SHARP protein to silence gene expression across the X chromosome. (B) ∼95% of all lncRNAs stably associate in compartments proximal to their transcriptional loci. These include the Kcnq1ot1, Airn, Pvt1, Tsix, and Chaserr lncRNAs, which silence expression of genes located proximal to their transcriptional loci within these compartments (left). Overall, these lncRNA compartments are present across the vast majority of DNA regions within the nucleus (right). (Panel B adapted from Quinodoz et al. 2020 with permission from the authors.) (C) SHARP forms dozens of discrete foci in the nucleus and these foci are disrupted upon deletion of its RNA-binding domain, resulting in diffusive localization of SHARP throughout the nucleus. (Panel C adapted from Quinodoz et al. 2020 with permission from the authors.)