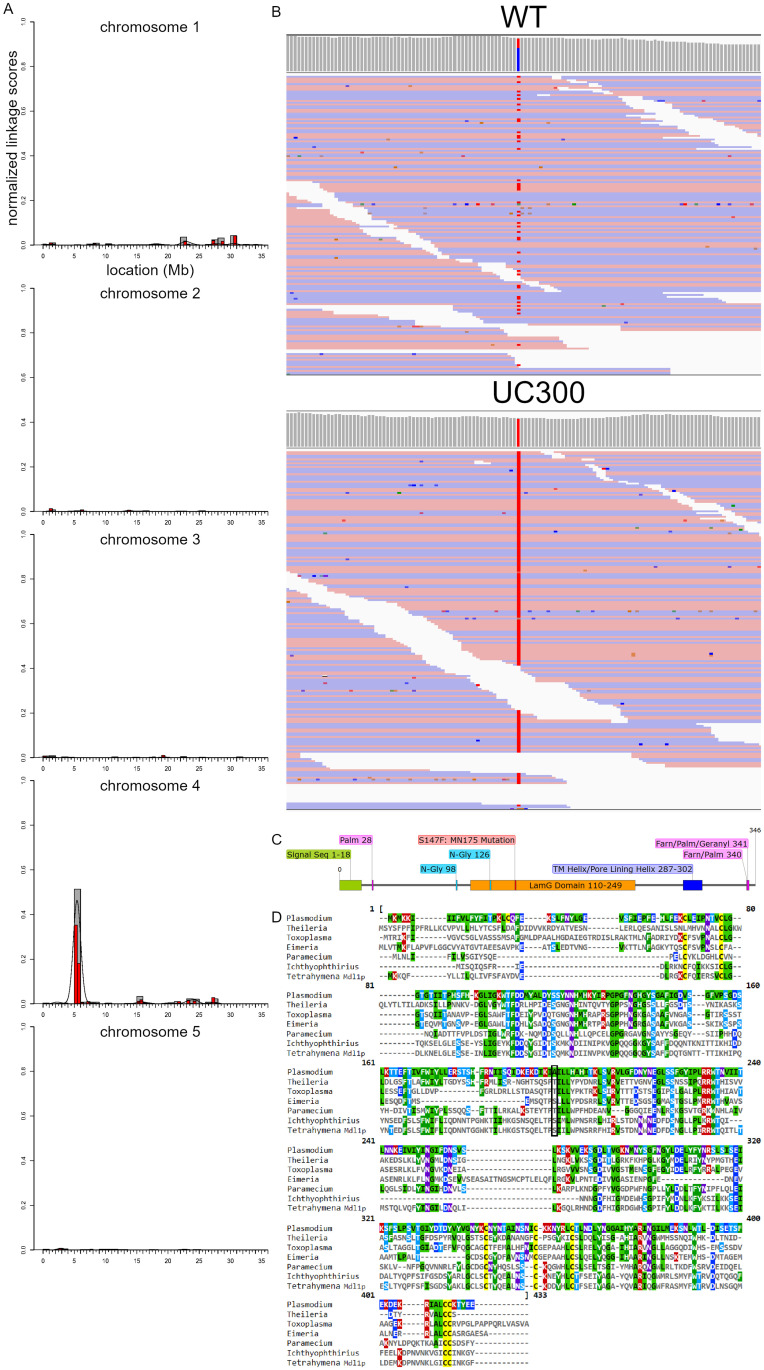
Fig 2. Mdl1p structure and expression.
A. The results of mapping of the causal DNA sequence variant for MN175 using ACCA [60]. Normalized linkage scores are shown along all five micronuclear chromosomes. Allelic cosegregation is increased on Chr 4 3-9Mb. B. Comparison (generated with IGV [http://software.broadinstitute.org/software/igv/]) between F2 pools with WT or MN175 phenotypes, of aligned sequencing reads around chr4: 5,364,873 (highlighted). At this site, reference read is G (blue) and variant read is A (red). C. Predicted features of Mdl1p. Residues 1–18: N-terminal signal sequence (from MEMSAT-svm). Residues 110–249: Laminin G domain (from NCBI BLASTp). Residues 287–302: transmembrane/pore-lining helix (from MEMSAT-svm). The protein lipid modification predictor GPS-Lipid (under medium threshold) identified three putative Mdl1p lipidation sites: palmitoylation at residue 28, farnesylation/palmitoylation at residue 340, and farnesylation/geranylgeranylation/palmitoylation at residue 341. The N-glycosylation predictor (NetNglyc 1.0 Server) identified two potential N-glycosylation sites at residues 98 and 126. The mutation in MDL1 in the MN175 strain results in substitution of serine by phenylalanine at residue 147. D. MUSCLE alignment of Mdl1p with homologs (identified via reciprocal BLAST searches) from Apicomplexans (Plasmodium falciparum XP_001349133.1, Theileria equi XP_004830018.1, Toxoplasma gondii XP_002370635.1, Eimeria tenella XP_013232975.1), and Ciliates (Paramecium tetraurelia XP_001433723.1 and Ichthyophthirius multifiliis XP_004039646.1). The alignment reveals conserved features including 3 pairs of cysteines. Two pairs are located N-terminal to the predicted transmembrane/pore-lining helix, while the 3rd pair is located near the C-terminus. The residue that is substituted by the mutation in MN175 is boxed.