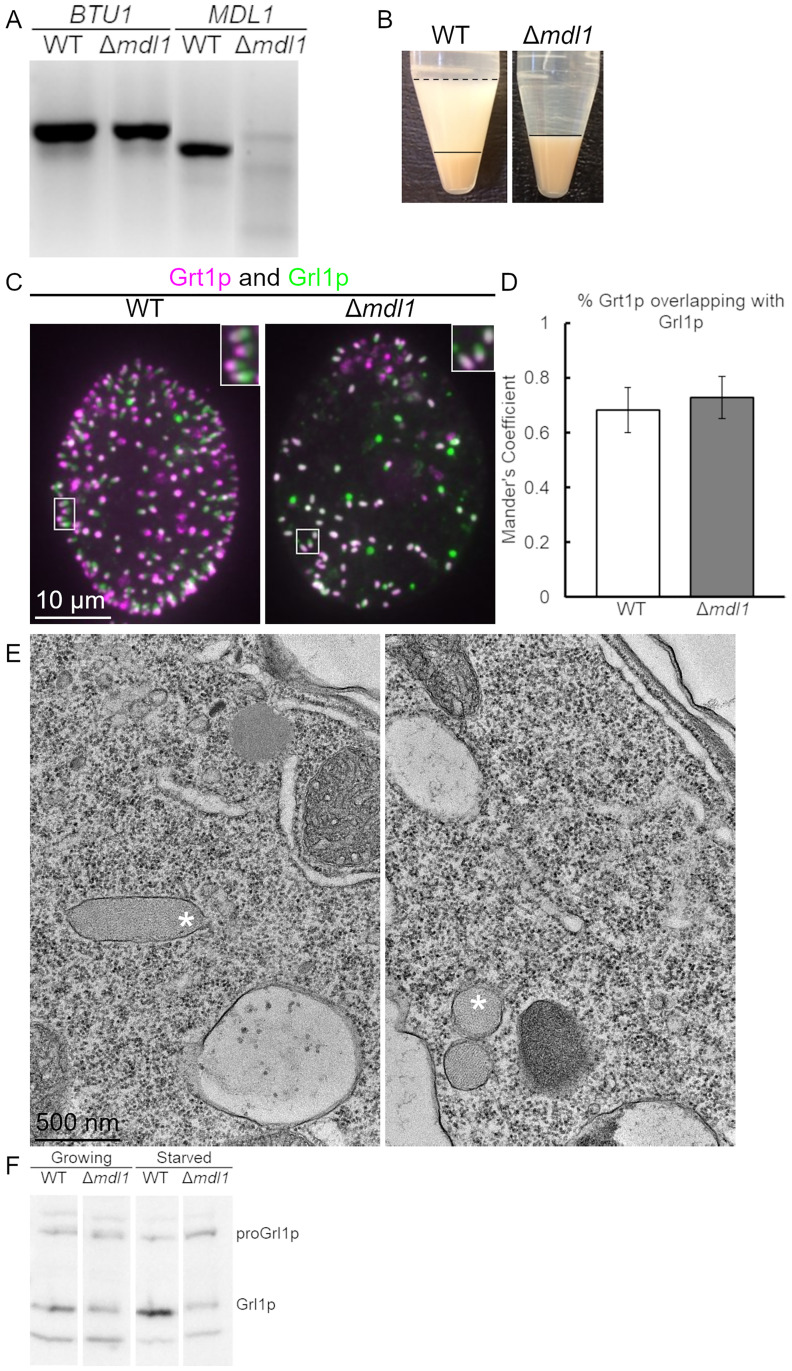
Fig 4. Analysis of Δmdl1 cells.
A. Δmdl1 cells have no detectable MDL1 transcript. cDNAs from wildtype and Δmdl1 were used as templates in PCR reactions with BTU1-specific primers as a control (lanes 1,2), and with MDL1-specific primers (lanes 3,4). The MDL1-specific primers flank intron 5. B. Δmdl1 cells are defective in induced mucocyst secretion. Equal numbers of wildtype and Δmdl1 cells were stimulated with dibucaine. The cell pellet is smaller in the wildtype sample compared to the mutant because in the former some cells remain trapped in the flocculent layer. The secretion defect in Δmdl1 is more severe than in MN175 (mdl1-S147F). C. Immunolocalization of mucocysts in Δmdl1. WT and Δmdl1 cells were immunolabeled with antibodies against both Grl1p (green) and Grt1p (fuchsia). Like in wildtype cells, the mucocysts in Δmdl1 are polarized with Grt1p concentrated at one tip. In contrast with wildtype or MN175 cells, the mucocysts in Δmdl1 are predominantly non-docked and localized throughout the cytoplasm. Scale bar is indicated. D. Quantification by Mander’s coefficient of overlap between Grt1p and Grl1p in WT and Δmdl1 cells. E. Thin section electron micrographs of mucocysts in Δmdl1 cells. The large majority of mucocysts (marked with *) are not docked at the plasma membrane. As in WT mucocysts, the contents are organized as a protein crystal. In the right panel, the two mucocysts shown were sectioned on their short axes. Scale bar is indicated. F. Δmdl1 contains reduced levels of mucocyst protein. Resolved whole cell lysates of wildtype and Δmdl1 cells, from both growing and starved cultures (104 cells/4-20% SDS-PAGE lane) were transferred to PVDF, and immunoblotted with antibodies against Grl1p. Compared to wildtype cells, Δmdl1 shows approximately 50% reduction of mature Grl1p in growing culture and 85% reduction in starved cultures.