Figure 3.
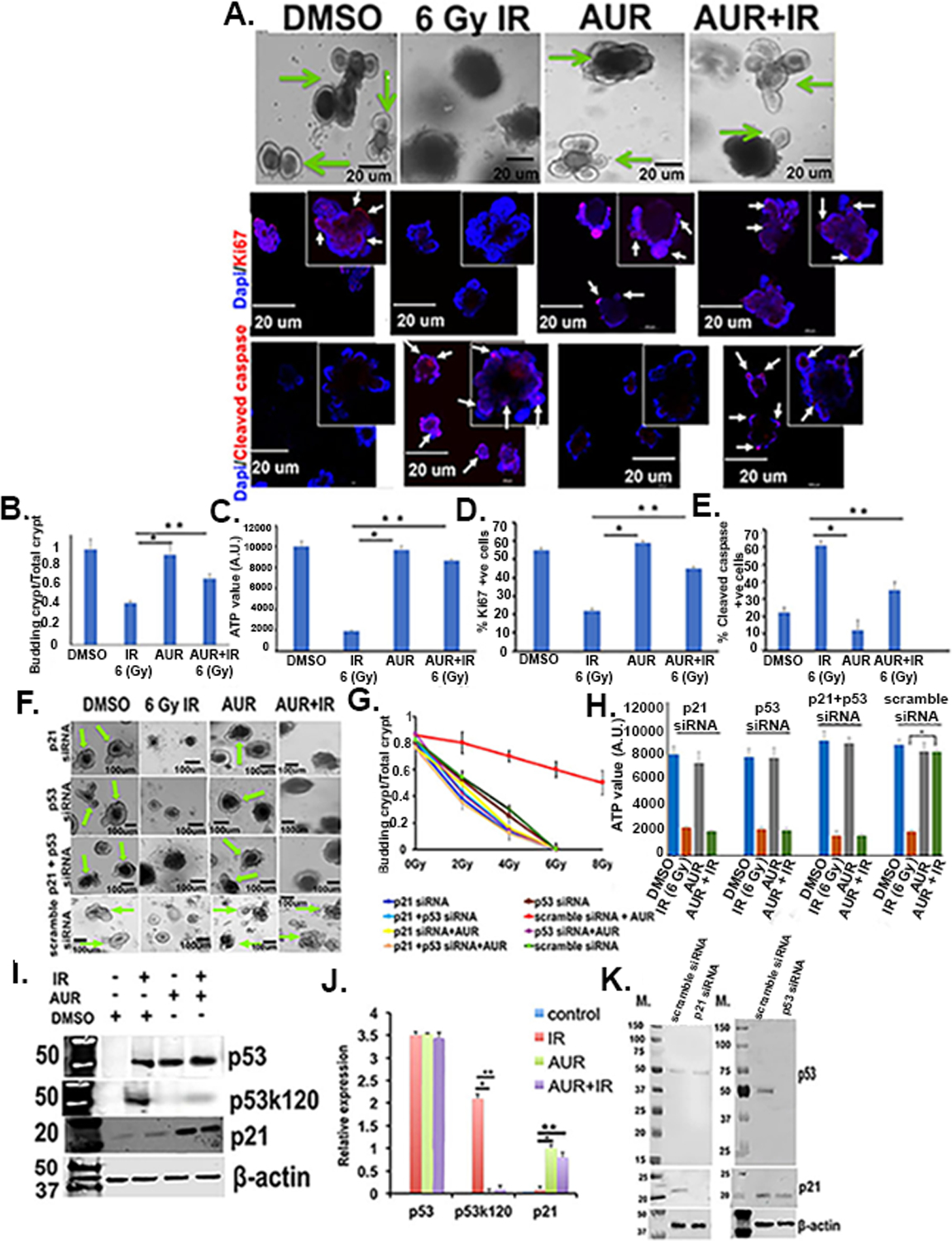
Auranofin protected human normal colon derived organoids from radiation toxicity. Organoids developed from surgical specimens of human non-malignant colon were treated with radiation (2–8 Gy), AUR (2 μmol/L) and the combination of both. Auranofin treatment did not have any toxic effect. Pretreatment with auranofin protected organoids from radiation-induced lethality by inducing crypt formation, compared to the radiation only group. A) Upper panel, Phase contrast microscopic images of organoids withall budding crypts indicated by an arrow). Middle panel: Confocal microscopic images of organoids stained with Ki67 (red color, indicated with arrow). Nucleus stained with DAPI (blue color). Lower panel: Confocal microscopic images of organoids stained with cleaved caspase (red color, indicated with arrow). Nucleus stained with DAPI (blue color). B) Histogram of budding crypt/total crypt ratio. The auranofin and AUR+IR groups had significantly higher budding crypt/total crypt ratio compared irradiated control (*p<0.0002 and **p<0.0006, respectively) (n=6 specimens). C) Histogram of ATP levels in organoids. The auranofin and AUR+IR groups had significantly higher ATP values compared to irradiated controls (*p<0.0004 and **p<0.0005, respectively). D) Histogram demonstrating percent Ki67 positive cells were significantly higher in auranofin and AUR+IR groups compared to irradiated controls (*p<0.0002 and **p<0.0006, respectively). E) Histogram demonstrating percent cleaved caspase positive (apoptotic) cells were significantly higher in irradiated control compared auranofin and AUR+IR treated groups (*p<0.0001 and **p<0.0003, respectively). F) Crypt organoid cells transfected with siRNA for p53, p21, or both did not respond to auranofin treatment. Note loss of budding crypt structures in these organoids even with auranofin treatment. G) Effect of auranofin pre-treatment on irradiated crypt organoid growth. Auranofin treatment improved the budding crypt/total crypt ratio in irradiated organoids compared to irradiated control. Organoids treated with siRNA for p53, p21, or both failed to improve budding crypt to total crypt ratio even with auranofin treatment. Treatment groups: 2 Gy + AUR vs 2 Gy (p<0.0007), 2 Gy +AUR vs 2 Gy + AUR + p53 siRNA (p<1E-04), 2 Gy + AUR vs 2 Gy + AUR + p21 siRNA (p<5.1E-05), 4 Gy + AUR vs 4 Gy (p<0.0003), 4 Gy + AUR vs 4 Gy + AUR + p53 siRNA (p<4.2E-04), 4 Gy + AUR vs 4 Gy + AUR + p21 siRNA (p<5.1E-06), 6 Gy + AUR vs 6 Gy (p<0.0004), 6 Gy + AUR vs 6 Gy + AUR + p53 siRNA (p<3.2E-07), 6 Gy + AUR vs 6 Gy + AUR + p21 siRNA (p<4.1E-06), 8 Gy + AUR vs 8 Gy (p<2.3E-07), 8 Gy + AUR vs 8 Gy + AUR + p53 siRNA (p<6.3E-07), 8 Gy + AUR vs 8 Gy + AUR + p21 siRNA (p<3.3E-08) (n=3 specimens). H) Histogram demonstrating that for irradiated organoids treated with p53 siRNA or p21siRNA or p53+p21 siRNA, auranofin pretreatment did not increase ATP levels. I) Immunoblot of total p53, acetylated p53 (p53k120) and total p21 protein expression. J) Histogram of densitometric analysis of immunoreactive bands representing p53, acetylated p53 (p53k120), total p21. Significant upregulation of p53k120 expression was noted in the IR group compared to auranofin alone (*p<6.4E-07) or AUR+IR group (**p<7.2E-07). Significant upregulation of p21 was noted in AUR alone (**p<0.0008) or AUR+IR group (**p<0.0006). K) Immunoblot of p53 and p21 expression in crypt organoid cells treated with siRNA for p53, p21 or scrambled siRNA. Representative immunoblot images from at least three independent experiments (n=3 specimens) with β-actin loading control.
