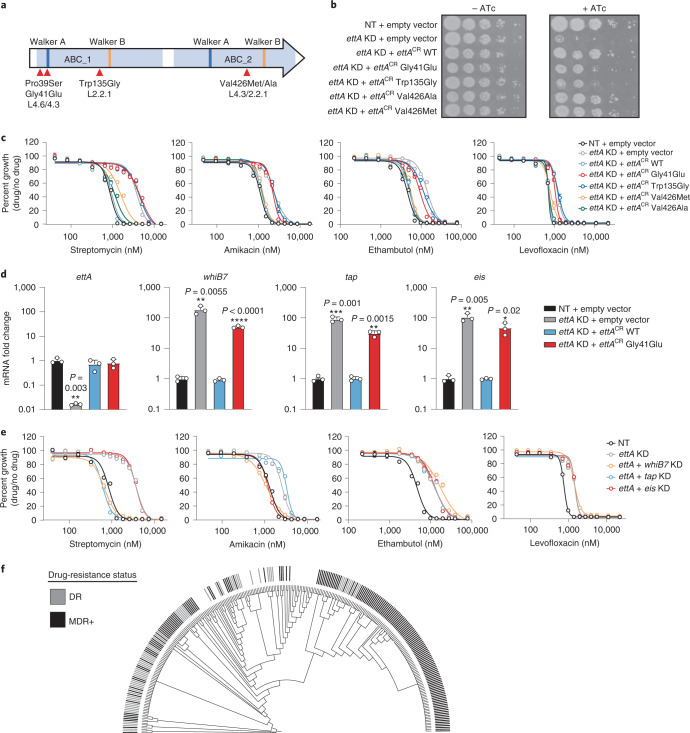
Fig. 5. Mutations in the translation factor EttA constitutively upregulate the whiB7 stress response and confer low-level, acquired multidrug resistance.
a, EttA domain organization. ABC domains, Walker A and Walker B motifs are highlighted in light blue, dark blue and orange, respectively. SNPs tested are highlighted with red arrows. b, Growth was monitored by spotting serial dilutions of each strain on the indicated media. The ettA CRISPRi strain was complemented with an empty vector or CRISPRi-resistant alleles harbouring the indicated ettA SNPs. c, Dose-response curves (mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 biological replicates) for strains harbouring ettA SNPs. d, Quantification (mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 biological replicates) of gene mRNA levels by RT-qPCR. Strains were grown +ATc for ~5 generations before collecting RNA. Statistical significance was calculated with Student’s t-test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. e, Dose-response curves (mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 biological replicates) for ettA single and dual knockdown strains. f, Phylogenetic tree of 291 Mtb clinical strains harbouring the ettA-Gly41Glu variant (Source Data Fig. 5). Genotypically predicted drug-resistance status is shown. DR, resistance-conferring mutations to rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide or ethambutol present; MDR+, resistance-conferring mutations to a minimum of rifampicin and isoniazid.