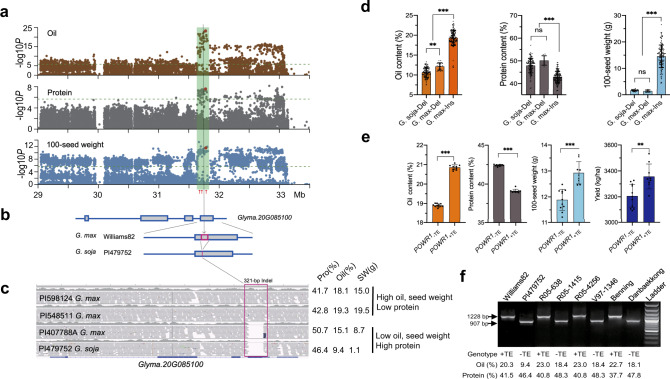
Fig. 1. Identification of the causative gene and allele underlying a large effect oil, protein, and seed weight QTL on chr20.
a Manhattan plots illustrating associations of oil, protein content, and 100-seed weight with SNPs and InDels across the 4-Mb interval on chr20. The 154-kb region is highlighted in green. The 321-bp InDel (red dots) and the significance threshold after Bonferroni correction (horizontal dotted lines) are shown. The red arrows at the bottom of the panel mark the locations of the three most significantly associated SNPs identified in GWASRIL. b Gene structure of Glyma.20G085100 with and without the 321-bp InDel (red box). c Sequencing read alignments of Glyma.20G085100 from two high oil/low protein accessions and two low oil/high protein accessions showing the 321-bp InDel. Seed oil (Oil), protein (Pro) content, and 100-seed weight (SW) of each accession are shown. d, e Allelic effect of the 321-bp InDel on oil, protein, 100-seed weight, and yield among the association panel d (n = 116, 8, and 154 for G. soja-Del, G. max-Del, and G. max-Ins, respectively) and among NILs (e) (n = 12). Trait values are shown as the mean ± SD (standard deviation). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA for the association panel and by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test for the NILs. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. Trait values are shown as the mean ± SD (standard Derivation). f PCR genotyping assay for the TE insertion in parental lines of four RIL populations. PCR amplicons of 1228 bp and 907 bp represent the presence and absence of the TE insertion, respectively. Genotypes for TE insertion, and oil and protein content for each accession are shown. This experiment was repeated twice. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.