Figure 6. Putative intracellular and intercellular mechanisms by which AVP and VIP signaling interact to reset the SCN molecular clock.
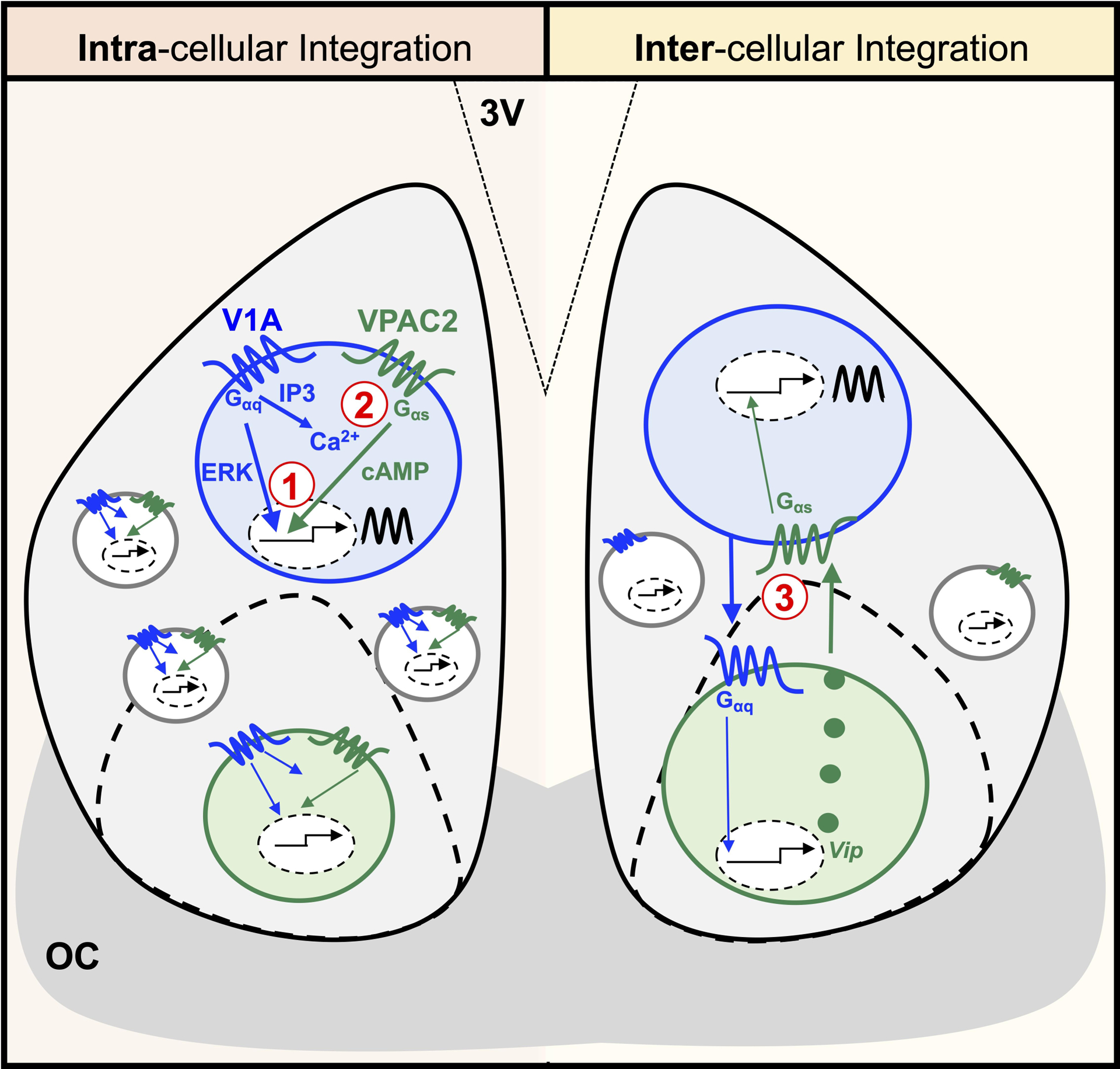
Left: At the single cell level, temporal and spatial co-expression may lead to interaction between V1- and VPAC2-induced signaling cascades. 1) Transcriptional integration: V1-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and VPAC2-activated cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB) signaling may synergistically regulate gene expression to shift the SCN clock. 2) Cytosolic integration: V1-activated diacylglycerol (DAG)/inositol triphosphate (IP3) could increase intracellular calcium to potentiate VPAC2-activated cAMP regulation of gene expression to shift the SCN clock. Right: At the network level, AVP and VIP signaling may interact through poly-synaptic circuits involving V1-induced up-regulation of Vip to shift the SCN clock. Note: Interactions between AVP and VIP neurons could occur either directly as shown or indirectly via connections with other SCN neurons. Further, other intracellular and intercellular signaling pathways may also be involved (not shown). 3V = third ventricle. OC = optic chiasm.
