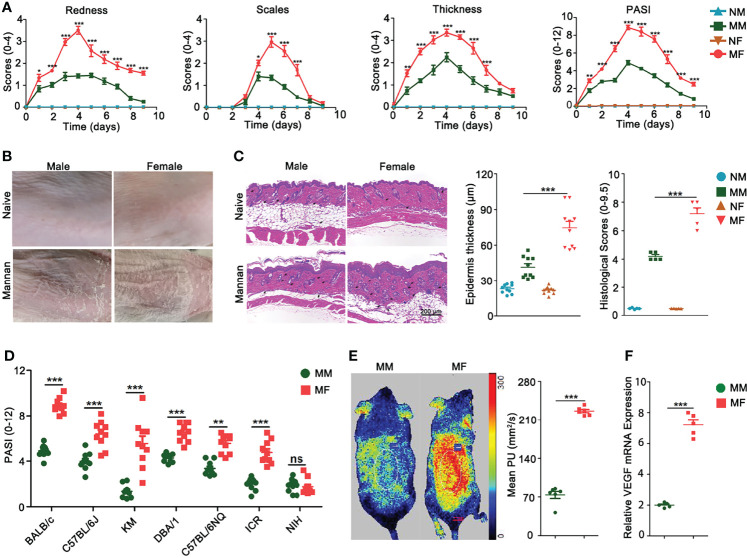
Figure 2.
Female mice developed more severe psoriasis. (A) Comparison of redness, scales, thickness, and total psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) between BALB/c female and male mice after mannan application (n = 15/group). (B) Representative pictures of psoriasis and naive skin from female and male mice on Day 5 (n = 12/group). (C) Comparison of H&E-stained skin sections, epidermal thickness, and histological scores between naive and psoriatic BALB/c female and male mice (n = 5/group). Scale bar: 200 μm. Infiltration of immune cells is marked by black arrows. (D) Comparison of total PASI at the peak of psoriasis in BALB/c, C57BL/6J, KM, DBA/1, C57BL/6NQ, ICR, and NIH female and male mice on Day 5 (n = 10/group). (E) Blood flow (n = 6/group) and (F) VEGF gene expression (n = 5/group) in the psoriatic skin of female and male mice on Day 5 after mannan application. Mean level of blood flow as well as VEGF gene expression in the PBS treated female and male mice was taken as one. Each experiment was repeated twice. Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired t test and n indicates number of mice. The data represent mean ± SEM. NM, naive male; MM, Mannan + Male; NF, Naive Female; MF, Mannan + Female. ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.