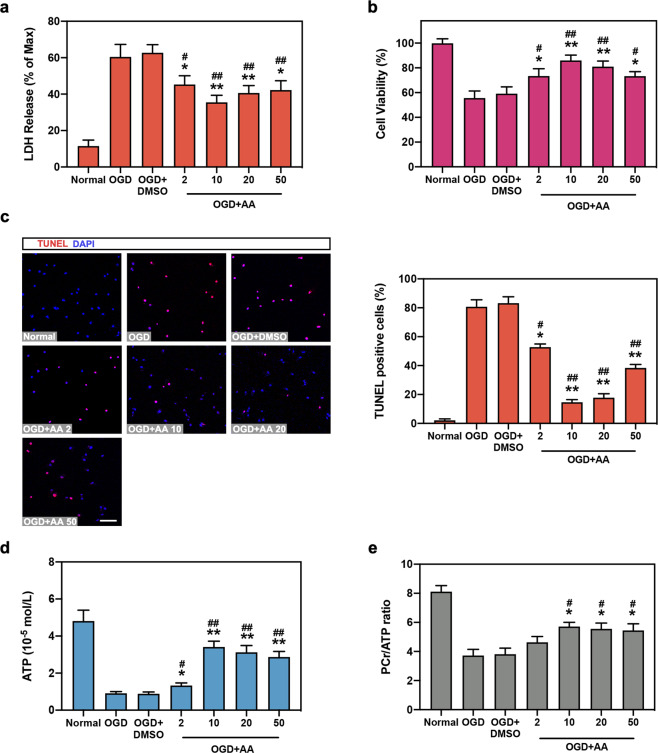
Fig. 1. Asiatic acid (AA) protects oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) cardiomyocytes in vitro.
Isolated neonatal mouse cardiomygocytes were divided into normal group, OGD for 12 h group, OGD + DMSO group, and OGD + concentration gradient of AA (2, 10, 20, and 50 μmol/L) group. (a, b) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release (a) and cell viability (b) were analyzed in cardiomyocytes. c The TUNEL assay was performed and analyzed in isolated mouse cardiomyocytes. Bar: 50 μm. d, e ATP (d) and phosphocreatine (PCr) levels were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, and the ratio of PCr/ATP (e) was calculated. n = 5–6 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. OGD group, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. OGD + DMSO group. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM.