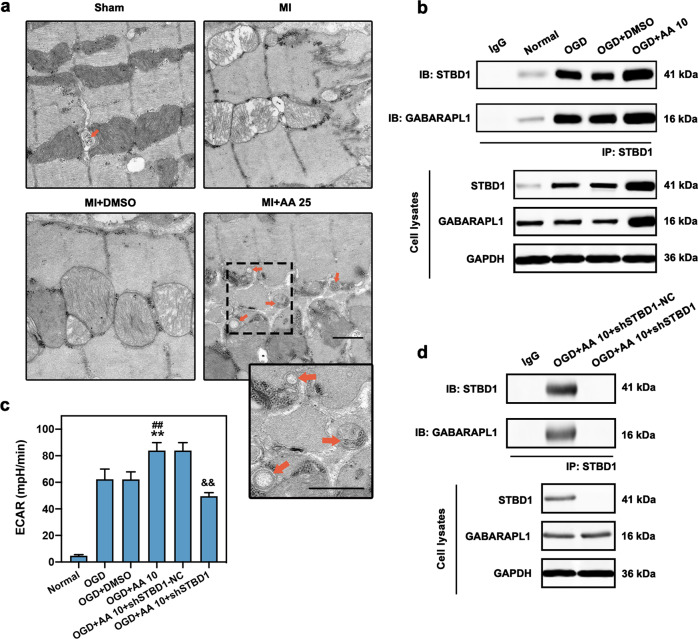
Fig. 5. Increased glycophagy is observed in OGD cardiomyocytes with AA treatment.
The dose of AA was 25 mg·kg−1·d−1 (AA 25) in vivo and 10 μmol/L (AA 10) in vitro. a Electron micrograph of glycophagosomes (orange arrows) in mouse MI (seven days) myocardium with AA 25 treatment; the box indicates the area enlarged on the lower right. Free glycogen particles were observed between myofibrils and mitochondria, and some glycogen particles were seen isolated in a glycophagosome, bar: 500 nm. b Isolated cardiomyocytes were treated with OGD, OGD + DMSO or OGD + AA 10, then immunoprecipitated with starch binding domain protein 1 (STBD1) antibody. STBD1 and GABA type A receptor-associated protein-like 1 (GABARAPL1) expression were determined using anti-STBD1 and anti-GABARAPL1 antibodies. c The extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) analysis via Seahorse XF96 extracellular flux analyzer was carried out to determine the glycolytic activity in isolated cardiomyocytes, n = 6 independent experiments. d Isolated cardiomyocytes were treated with AA 10 and shSTBD1-NC or shSTBD1 and then immunoprecipitated with STBD1 antibody. **P < 0.01 vs. OGD group, ##P < 0.01 vs. OGD + DMSO group, &&P < 0.01 vs. OGD + AA 10 + shSTBD1-NC group. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. IB immunoblotting, IP immunoprecipitation.