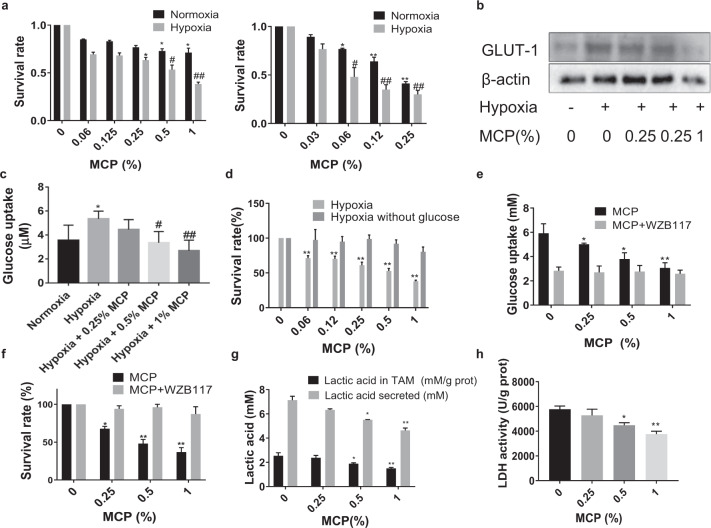
Fig. 1. MCP inhibited the survival of TAM in hypoxia by reducing glucose uptake via downregulation of GLUT-1.
a TAM were treated with MCP at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. Oxygen deprivation (1% O2) was achieved by culturing cells in hypoxic chambers. Effects of MCP on cell viability of TAM was detected by CCK-8 assay. Left: THP1-derived TAM; right: BMDM-derived TAM. b Effect of MCP on the expression of GLUT-1 in TAM at the indicated concentrations for 24 h was detected by Western blotting. c The glucose uptake of TAM treated with MCP in hypoxia was determined by glucose assay kit. d Effect of MCP on cell viability of TAM in glucose-free medium at the indicated concentrations for 24 h was detected by the CCK-8 assay. e The glucose uptake of TAM treated with MCP or/and WZB117 (10 μM) under hypoxia for 24 h was detected by the glucose assay kit. f Effect of MCP or/and WZB117 on cell viability of TAM in hypoxia at the indicated concentrations for 24 h was detected by the CCK-8 assay. g The lactic acid in medium supernatant of TAM and the content of lactic acid in TAM in hypoxia for 24 h were detected by lactic acid assay. h The LDH activity in TAM in hypoxia for 24 h was detected by LDH assay. All the experiments have been repeated three times. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. normoxia control group of; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, vs. respective hypoxia control group.