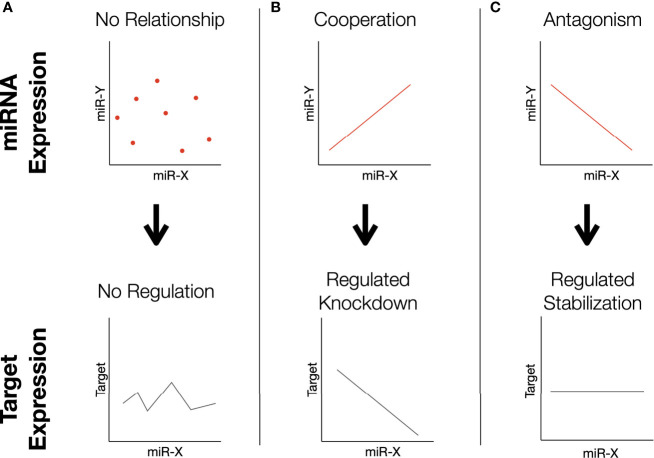
Figure 4.
Proposed dynamics of miRNA correlations. In this correlation-based analysis, we assume miRNAs influence the same direct phenotype related to some aspect of fertility. Note that this mechanism may manifest by the correlated pairs targeting the same gene (as depicted), or different aspects of a functional pathway. (A) Two miRNAs whose expression is not correlated may result in variable expression of the shared target. (B) Cooperating miRNAs effectively regulate knockdown: low levels of both permits high expression, high levels of both silence it. (C) Antagonistic miRNAs have inverse expression patterns; high levels of one are associated with low levels of the other. The relationship ensures moderated expression of the target, as the overall abundance of both miRNAs is balanced.