Figure 3.
Calcium storage in biofilm cells
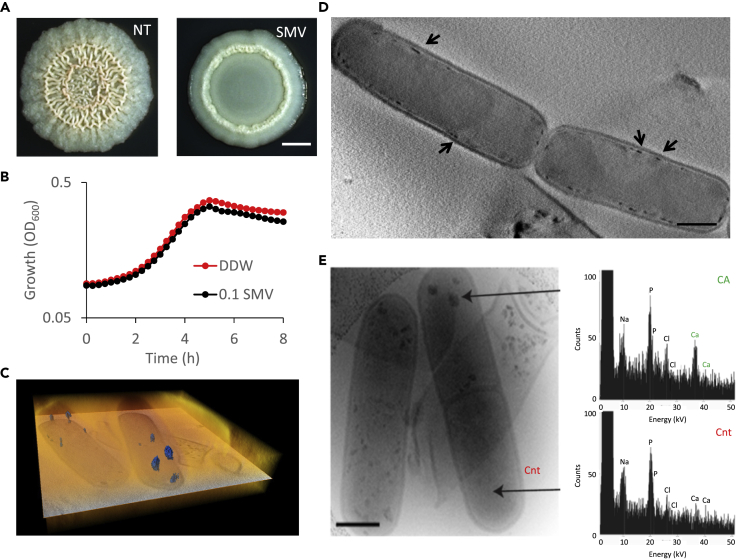
(A) Light microscopy images of 5-day-old B. subtilis biofilm colonies grown with calcium, and supplemented with calcium uptake inhibitor (0.1 mg/mL sodium metavanadate (SMV)), as indicated. NT indicated untreated culture. Scale bar – 2 mm. A representative image (out of n = 3 experiments) is shown.
(B) The effect of inhibiting calcium uptake on planktonic growth. B. subtilis was grown shaking in liquid B4 medium with calcium, supplemented with 0.1 mg/mL SMV, as indicated. Results are averages of nine wells. Bars represent standard deviations. A representative experiment (out of n = 3 experiments) is shown.
(C) Volume rendering (orange) and a single orthoslice (greyscale) through the center of the volume, from a 3D CSTET reconstruction. The calcium-rich deposits are artificially colored (blue).
(D) A 30-nm thick virtual slice through a CSTET 3D reconstruction of B. subtilis cells showing intracellular calcium-rich deposits (arrows). Scale bar – 400 nm. A representative field (out of n = 20 fields, from three experiments) is shown.
(E) Left panel - Bright-field STEM image of representative B. subtilis biofilm cells showing cellular calcium deposits, from a colony grown 10 days on B4-Ca2+ agar. The black arrow indicates the cell used for EDX analysis in panels (B-C). Right panel – EDX analysis of the calcium deposits. A representative mineralizing cell imaged (out of n = 50 cells, from four independent experiments performed with EDX is shown.