Figure 1.
Systematic screening of the GRACE PK collection to identify kinases important for fungal growth
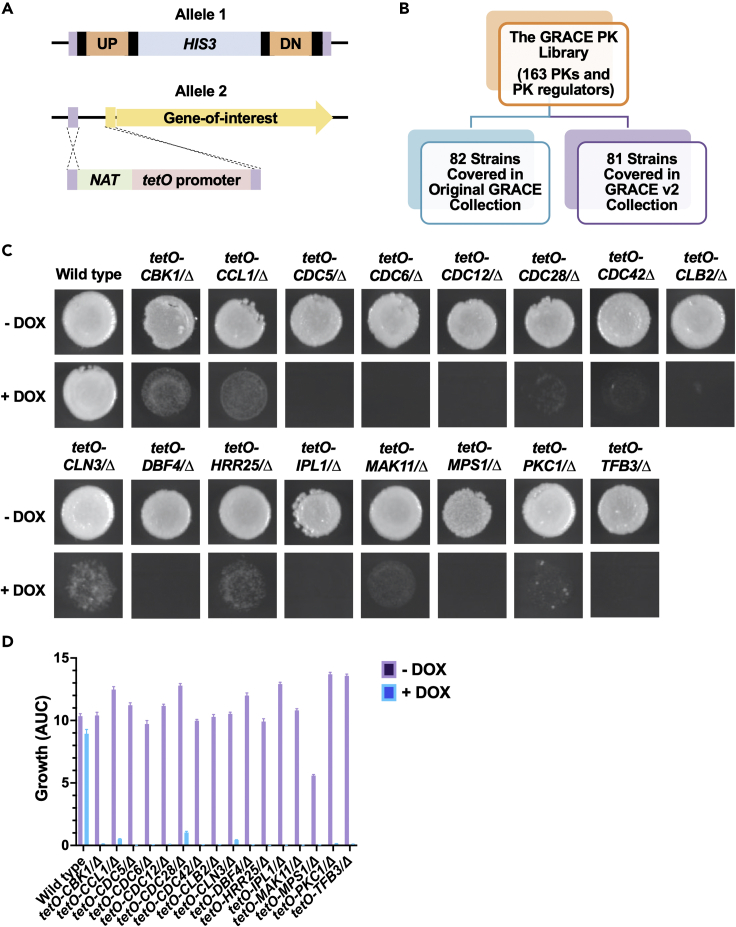
(A) Schematic of GRACE strains. In this system, one allele of a given gene is deleted and the second allele in the diploid genome is placed under the control of a tetracycline-repressible promoter (tetO).
(B) Leveraging the GRACE (blue) and GRACEv2 (purple) libraries provides comprehensive coverage of C. albicans PKs and select PK regulators.
(C) Colony images of hits from the essentiality screen. The GRACE PK library was grown overnight in YPD with and without DOX (100 μg/mL). Cells were then transferred onto YNB agar with or without DOX (100 μg/mL) and following 48 h of incubation at 30°C, images were taken using a ChemiDoc XRS + imager. Sixteen of the 163 mutant strains exhibited severe growth defects following DOX-mediated transcriptional repression.
(D) Growth curve validation of screening hits. All 16 GRACE strains identified as hits were subjected to an overnight growth in YPD at 30°C and a second overnight growth in YPD with 100 μg/mL of DOX before cells were pinned with a microplate replicator into 96-well plates containing liquid YNB supplemented with 100 μg/mL of DOX . Cells were incubated for 24 h and the optical density (OD600) of each well was measured every hour. Area under the curve (AUC) was calculated by the trapezoidal method using GraphPad Prism. Error bars represent SEM of technical quadruplicates. Testing was repeated as an independent biological replicate to confirm results.