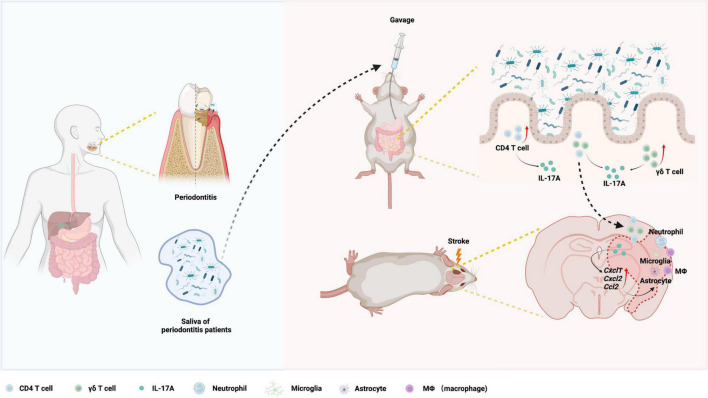
FIGURE 7.
Working model for the exacerbation of ischemic stroke by periodontitis salivary microbiota. Periodontitis salivary microbiota increases IL-17A-producing cells in the small intestine, which contain CD4+ T cells and TCR-γδ+ T cells. Increased migration of IL-17A-producing cells from the gut to the brain elevates post-ischemic chemokines (Cxcl1, Cxcl2, and Ccl2) and ultimately infiltration and activation of immune cells (macrophages/microglia, astrocyte, and neutrophils) in ischemic brain, leading to exacerbated neuroinflammation and ischemic stroke phenotype.