Extended Data Fig. 8 |. Model of the unique telomere protection mechanism in ES cells.
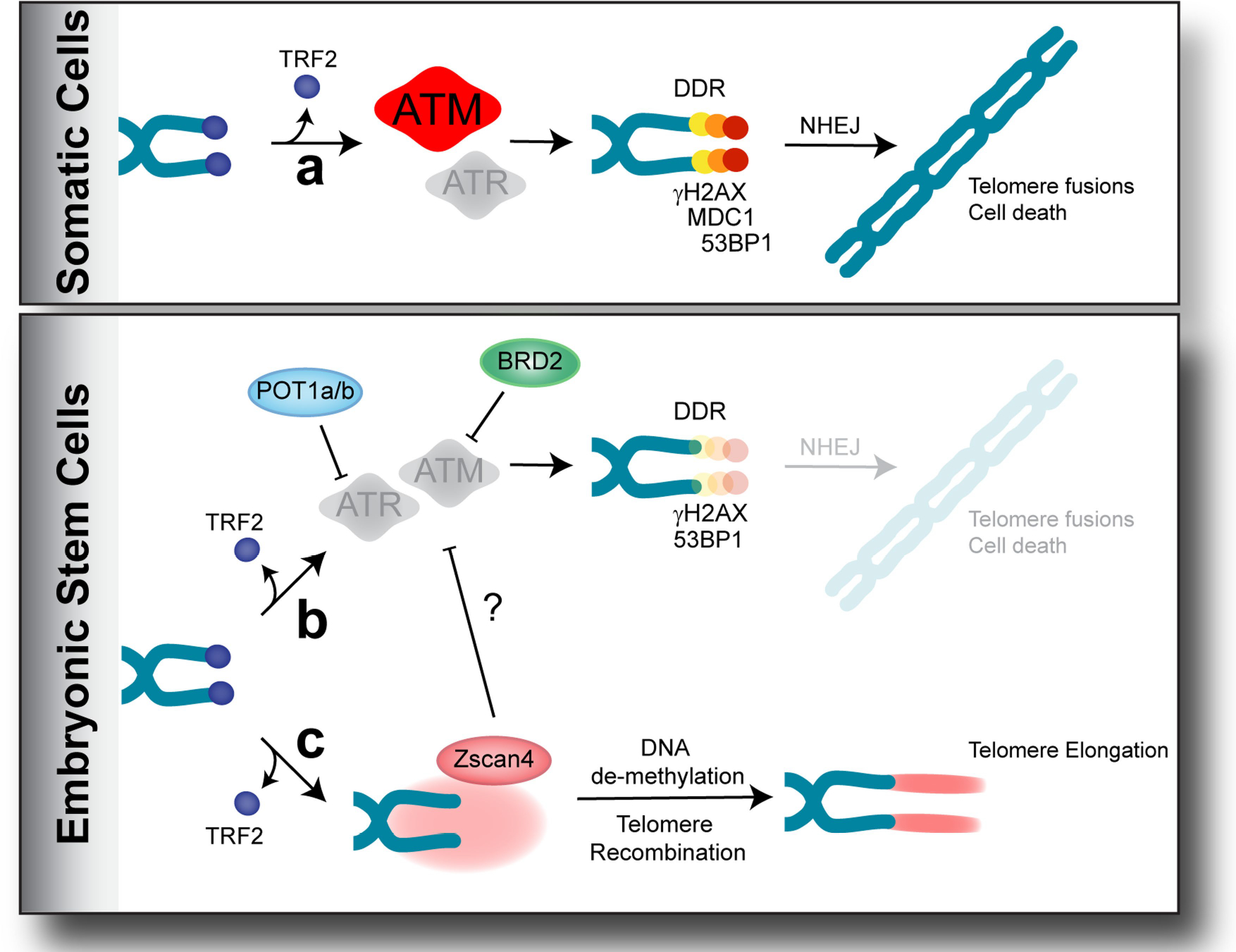
a, Overview of the DDR in response to TRF2 depletion in somatic cells. In response to uncapped telomeres, ATM kinase initiates DDR, leading to end-to-end fusions via the NHEJ pathway. b, POT1A, POT1B and BRD2ensure genomic stability in pluripotent mouse ES cells by inhibiting the activities of ATM and ATR kinases. As a result, mild DDR is not enough to cause end-to-end fusions. c, Increased expression of Zscan4—a cluster of two-cell-signature genes—might result in recombination-based telomere elongation. Alternatively, the ZSCAN4 -dependent inhibition of the ATM and ATR kinases at TRF2-depleted telomeres of ES cells ensures telomere stability.
