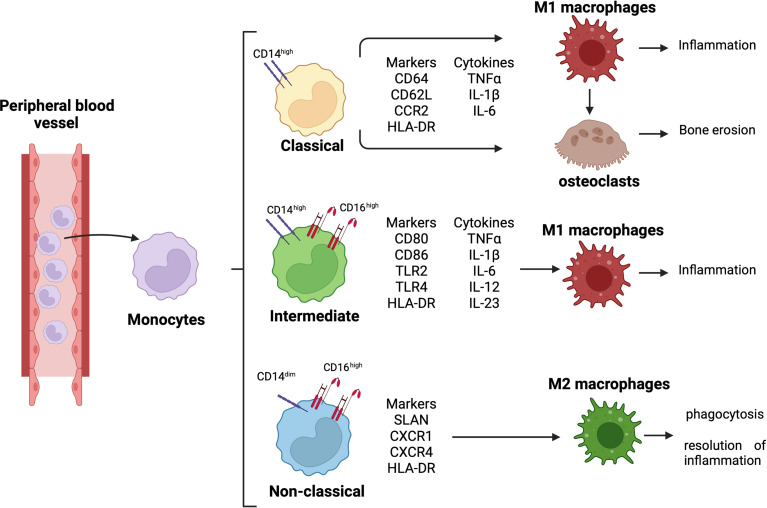
Figure 1.
Monocyte differentiation and related role in RA pathogenesis. Differentiation of circulating monocytes in their three subsets, classical (CD14high), intermediate (CD14highCD16high), and non-classical (CD14dimCD16high) monocytes. Classical monocytes can differentiate into pro-inflammatory macrophages and osteoclasts, contributing to synovial tissue inflammation and bone erosion; intermediate monocytes differentiate into pro-inflammatory macrophages contributing to tissue inflammation; non-classical monocytes differentiate into anti-inflammatory macrophages promoting phagocytosis and resolution of inflammation.