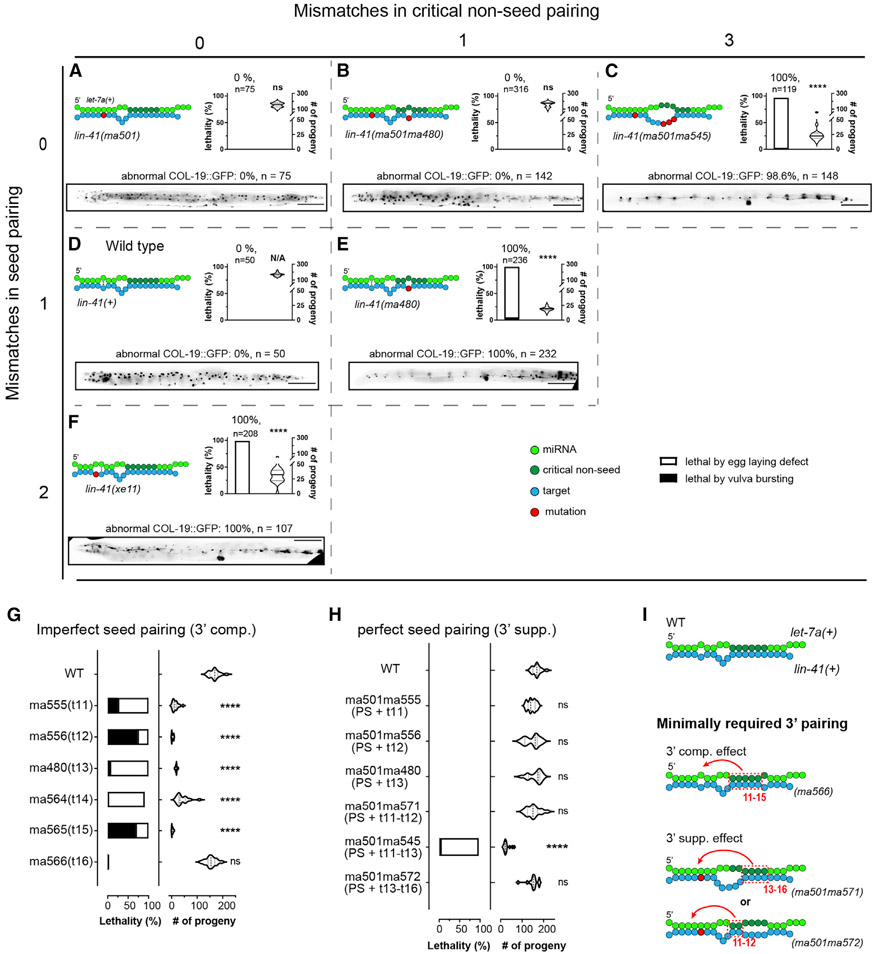
Figure 6. Critical 3′ non-seed pairing and seed pairing together contribute to let-7a target repression.
(A–F) Pairing configurations of let-7a to the lin-41 LCSs and associated phenotypes for lin-41(ma501) (A), lin-41(ma501ma480) (B), lin-41(ma501ma545) (C), lin-41(+) (D), lin-41(ma480) (E), and lin-41(ex11) (F), arranged in a matrix based on mismatches in seed (vertical axis) and critical non-seed region (horizontal axis). Each panel includes pairing pattern (top left), vulva defect (young adult lethality and number of progeny, top right), and heterochronic phenotype (bottom). Scale bars, 100 μm.
(G and H) Vulva integrity of lin-41 LCSs mutants with 3′ pairing mismatches in the context of imperfect (G) and perfect seed pairing (H).
(I) Models depicting the minimal pairing requirement for 3′ compensatory and 3′ supplemental effects. Statistical significance indicates relative to WT. Phenotypes were tested at 25°C. All of the lin-41 alleles tested in this figure do not contain a fluorescent protein tag.
Details of the phenotypes available in Table S1.