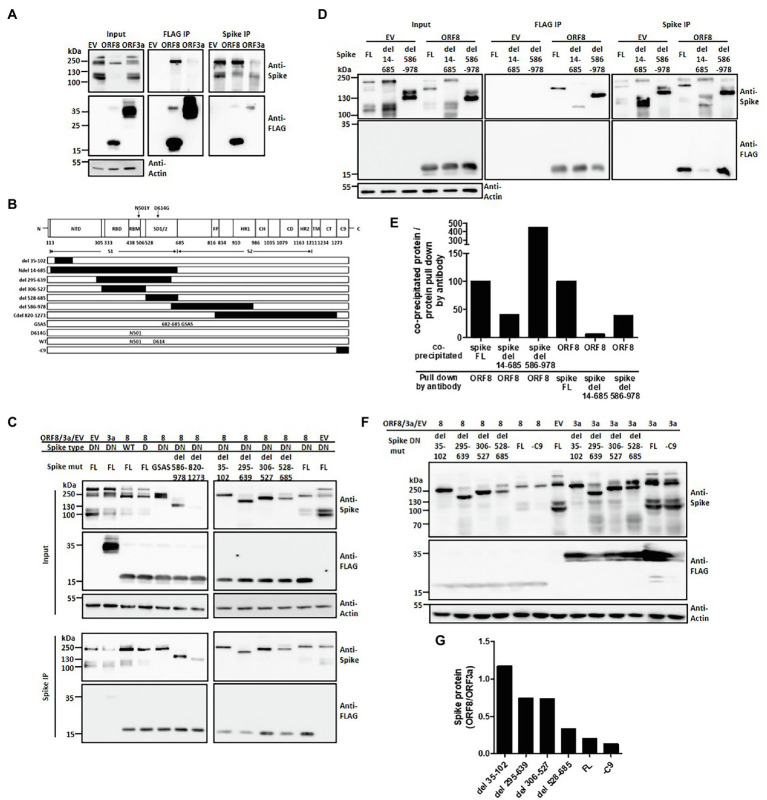
Figure 3.
ORF8 interacts with the spike protein at different domains. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with the plasmids described in each figure, and the cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoprecipitation using an antibody against the FLAG tag or spike protein. In all following immunoprecipitation results, immunoblots were obtained using total cell lysates (input), and the proteins were pulled down by Protein G Dynabeads conjugated with the indicated antibody (IP). (A) Representative immunoprecipitation data obtained using either anti-FLAG or anti-spike antibodies are shown. EV: empty vector. (B) A series of spike proteins with different mutations or deletions were constructed for the experiments described in the cartoon figure. Schematic figure presenting the domain arrangement of the spike protein was adapted from Duan et al. with few modifications. NTD: N-terminal domain; RBD: receptor-binding domain; RBM: receptor-binding motif; SD1/2: subdomain 1 and 2; FP: fusion peptide; HR1 and HR2: heptad repeat 1 and 2; CH: central helix; CD: connector domain; TM: transmembrane domain; CT: cytoplasmic tail; C9: C9 tag. The black boxes shown in this figure represent the deleted regions of the spike protein. (C) A series of immunoprecipitation experiments focusing on different spike variants or deletions were performed using a polyclonal anti-spike antibody. (D) An immunoprecipitation experiment was performed using the full-length or the mutated spike protein with deletion of the S1 (del 14-685) or S2 region (del 586-978) was shown. (E) Meanwhile, the intensity of interaction between ORF8 with different mutations of the spike proteins shown in (D) was evaluated by the evaluation of the ratio between the protein level of the co-precipitated protein vs. the protein directly pull down by the indicated antibody. (F) The spike protein expression levels were compared between ORF8- and ORF3-transfected cells by using immunoblotting and (G) the spike protein expression level in between both groups was evaluated by using the ImageJ software. Abbreviations of the spike mutants shown in (C–F) are as following: DN: D614G/N501Y; D: D614G; GSAS: point mutations created at 682–685 amino acids; FL: full length; -C9: spike protein without C9 tag at its C-terminal. And del 14-685, del 586-978, del 35-102, del 295-639; del 306-527; del 528-685 represent the deletion regions of the spike protein.