Extended Data Figure 6. SRGAP2C expression selectively increases synaptic density on apical dendrites.
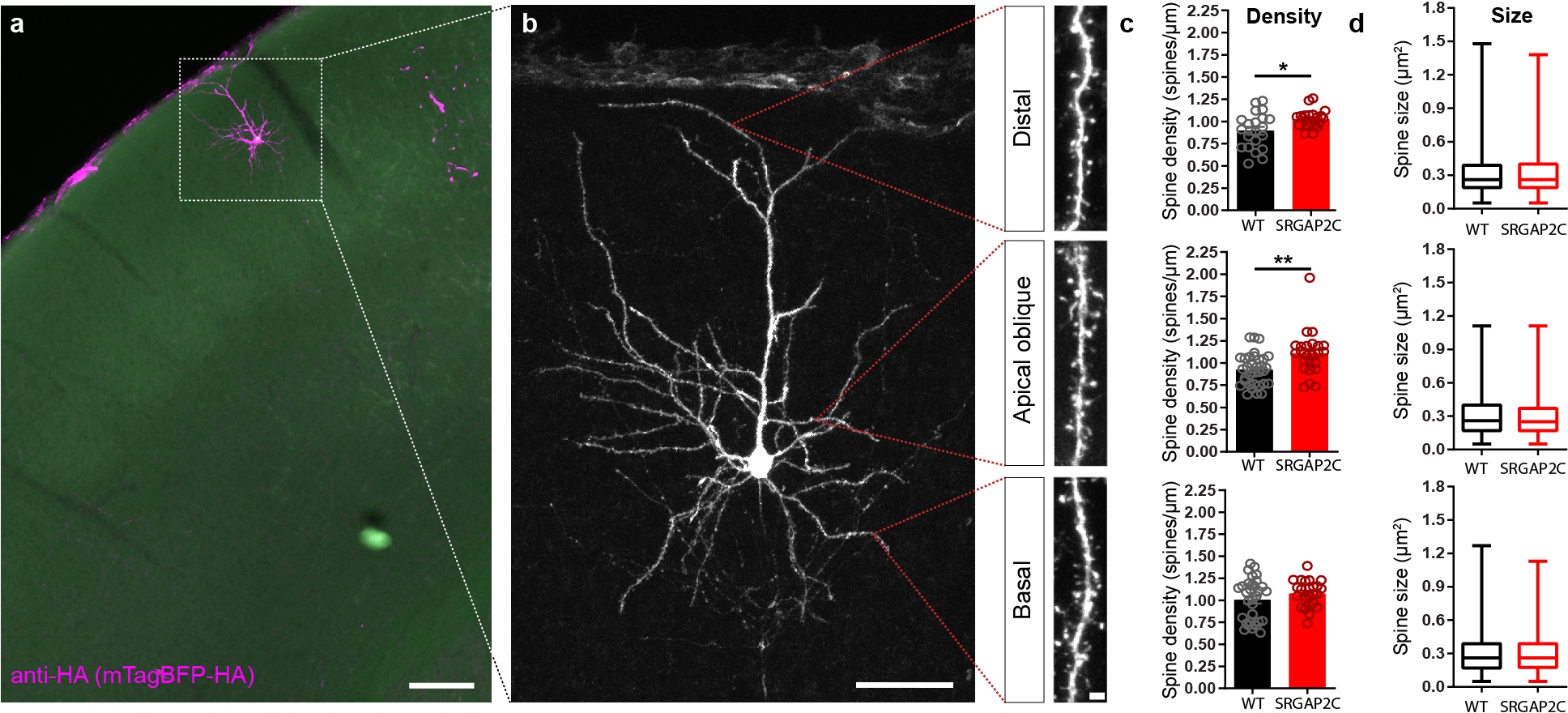
(a) Coronal section stained for HA showing sparse labeling of a layer 2/3 cortical pyramidal neuron in the barrel field of the primary somatosensory cortex. Scale bar, 150 μm. (b) Higher magnification of neuron in (a). Red dotted lines indicate approximate location where spine density and size were quantified for distal, apical oblique, and basal dendritic compartments. Panels on right show high magnification images of dendritic segments on which spines can clearly be identified. Left panel scale bar, 50 μm. Right panel scale bar, 2 μm. (c) Spine density is increased for distal, and apical but not basal dendritic segments. (P = 1.92 × 10−2 for distal, P = 1.5 × 10−3 for apical oblique, P = 0.3 for basal; distal: n = 21 segments for WT and SRGAP2C, apical oblique: n = 33 segments for WT and n = 24 segments for SRGAP2C, basal: n = 32 segments for WT and n = 24 segments for SRGAP2C). Bar graph plotted as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-sided Mann-Whitney test. (d) Spine size is not significantly changed in adult SRGAP2C expressing layer 2/3 cortical pyramidal neurons. Data shown as box-and-whisker plots. Center line indicates median, box edges represent first and third quartiles, and whiskers represent minimum and maximum values (distal: n = 1273 spines for WT and n = 1083 spines for SRGAP2C, apical oblique: n = 2401 spines for WT and n = 1650 spines for SRGAP2C, basal: n = 2286 spines for WT and n = 1448 spines for SRGAP2C).
