FIGURE 1.
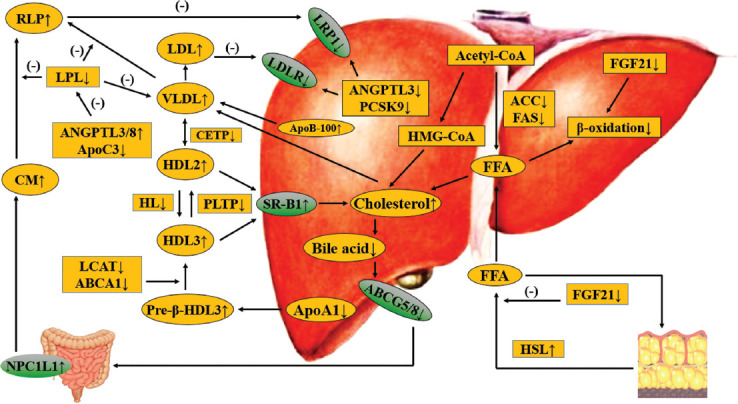
Effects of thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormones on lipid metabolism in hypothyroidism. Thyroid hormones decrease in hypothyroidism, then DNL and the activity of HMGCR reduces, leading to declined cholesterol production, but FFA β-oxidation also decreases. TH reduction reduces the activity of CYP7A1 and ABCG5/8 to reduce cholesterol clearance. In general, TG-rich VLDL level is increased in hypothyroidism, and the elevation of NPC1L1 concentration leads to an increase of TG-rich CM. DNL: de novo lipogenesis; FFA: Free fatty acid, TG: triglyceride; RLP: Remnant lipoprotein; NPC1L1: Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 protein; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein; ANGPTL3/8: Angiogenin-like protein3/8; ApoC3: Apolipoprotein C3; CETP: Cholesterol transport protein transporter; HL: Hepatic lipidosis; PLTP: Phospholipid transfer protein; LCAT: Lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase; ABCA1: ATP-binding cassette transporter A1; SRB1: Scavenger receptor b1; FGF19/21: Fibroblast growth factors 19/21; HMG-CoA: 3-Hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; CM: Chylomicron; ABCG5/8: ATP-binding cassette transporter G5/8; CYP7A1: Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; HMGCR: HMG-COA reductase
