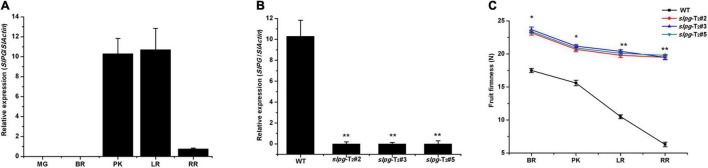
FIGURE 2.
Expression patterns of SlPG and phenotype identification of tomato slpg mutant. (A) Expression of SlPG in fruit at different developmental stages: MG, BR, PK, LR, and RR; (B) Expression of SlPG in WT plants and T2 homozygous slpg mutants (slpg-T2#2, slpg-T2#3, and slpg-T2#5). Relative transcript levels of SlPG were analyzed by qRT-PCR and normalized to SlActin. Quantitative PCR data represent means values for three independent biological replicates (n = 3); (C) Phenotype of enhanced fruit firmness at different fruit development stages in slpg mutants. The fruit firmness values represent the means ± standard error (SE) of 20 individual fruit per line at each stage. * and ** indicate significant differences between WT plants and T2 homozygous slpg mutants (slpg-T2#2, slpg-T2#3, and slpg-T2#5) with p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively, as determined by t-test.